摘 要
多序列比对是现代生物信息学研究的核心问题,通过多序列比对,能发现蕴藏于一个基因家族的普遍遗传规律。本文先研究了三种双序列比对算法,再研究经典的多序列比对算法CLUSTAL,详细分析并进行实现。由于多序列比对需要大量的计算资源,如果序列簇很多,将消耗大量的运行时间。CLUSTAL算法主要有两两比对、构建向导树和渐近比对三个步骤,本文利用CUDA平台调度GPU提供的并行计算能力,优化算法第一个步骤,并行调用双序列比对算法进行两两比对。在多组实验与结果统计表明,当序列数目超过一定量(30条长约30个碱基的序列左右)时,本文提出的基于CUDA的多序列比对并行算法相比于原始的CLUSTAL算法,有较高精度同时还拥有较高的运行效率。
关键词 多序列比对算法;CUDA计算;CLUSTAL;序列比对
Abstract
Multiple sequence alignment is the core of modern bioinformatics research. Through multiple sequence alignment, we can find the general genetic law contained in a gene family. This paper first studies three kinds of double sequence alignment algorithms, and then studies the classic multiple sequence alignment algorithm CLUSTAL. Because multiple sequence alignment requires a lot of computing resources, if there are many sequence clusters, it will consume a lot of running time. Cluster algorithm has three steps: pairwise comparison, constructing guide tree and asymptotic comparison. In this paper, we use the parallel computing power provided by CUDA platform scheduling GPU to optimize the first step of CLUSTAL, and call the double sequence alignment algorithm in parallel for pairwise alignment. Many experiments and results show that when the number of sequences exceeds a certain amount (about 30 sequences of about 30 bases in length), compared with the original CLUSTAL algorithm, the CUDA based parallel algorithm has higher accuracy and higher efficiency.
Keywords Multiple Sequence Alignment Algorithm; CUDA; CLUSTAL; Sequence Alignment
目 录
第1章 绪论
1.1 引言
1.2 序列比对
1.2.1 双序列比对算法
1.2.2 多序列比对算法
1.3 CUDA平台
1.4 本文研究目标与内容
第2章 双序列比对算法
2.1 序列比对
2.1.1 引入序列比对的原因
2.1.2 全局比对与局部比对
2.2 Needleman-Wunsch(NW)算法
2.2.1 NW算法简介
2.2.2 NW算法举例介绍
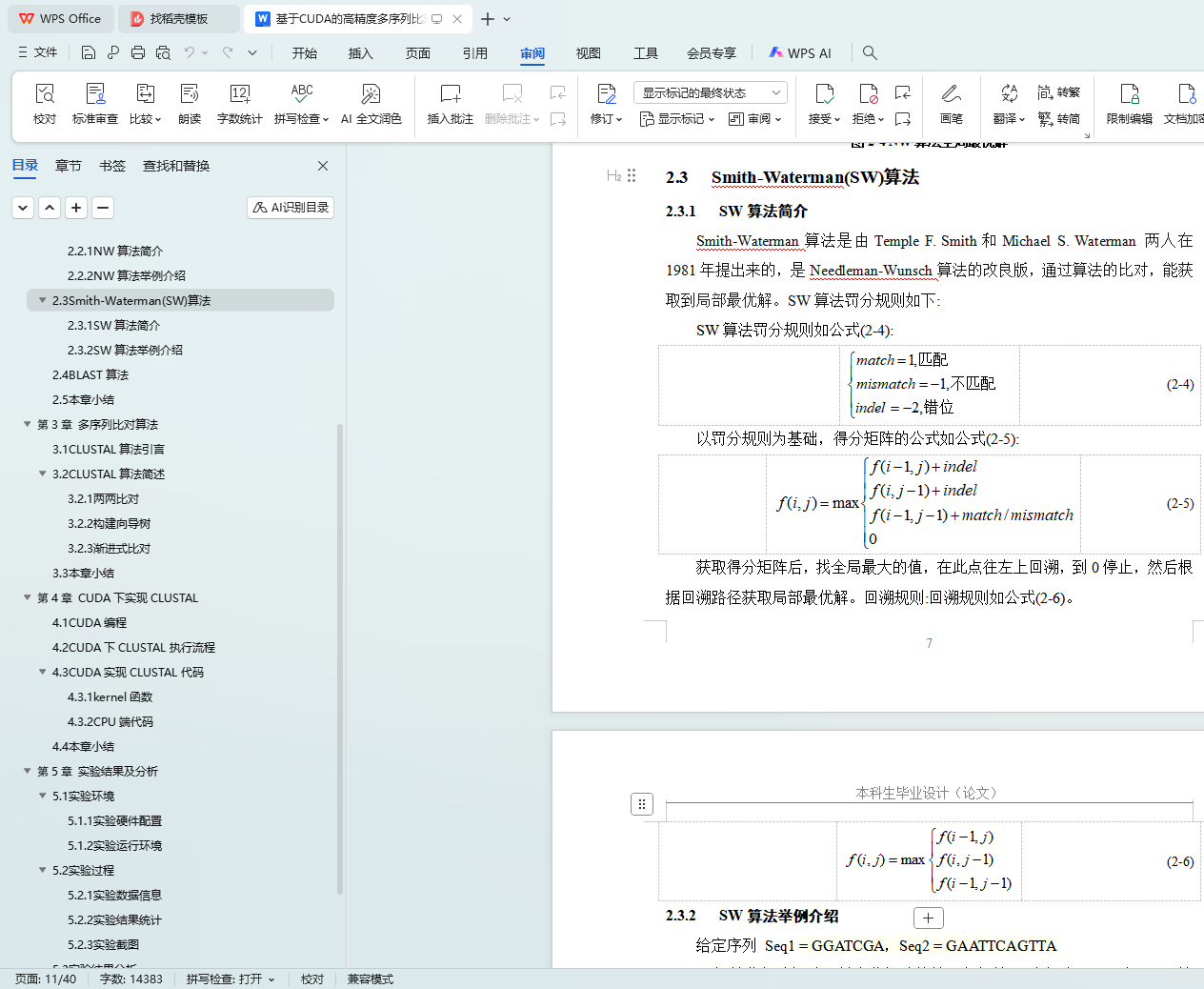
2.3 Smith-Waterman(SW)算法
2.3.1 SW算法简介
2.3.2 SW算法举例介绍
2.4 BLAST算法
2.5 本章小结
第3章 多序列比对算法
3.1 CLUSTAL算法引言
3.2 CLUSTAL算法简述
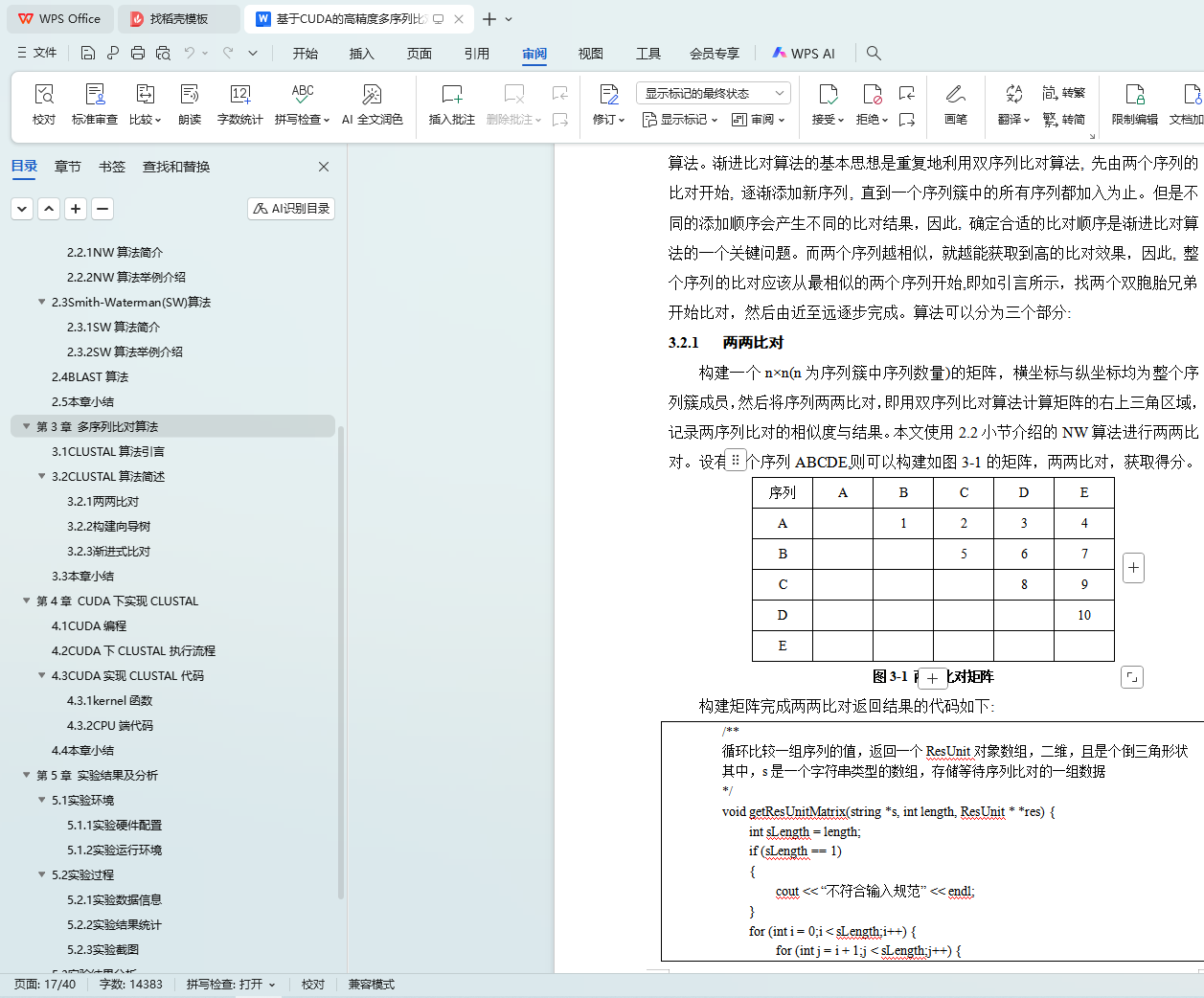
3.2.1 两两比对
3.2.2 构建向导树
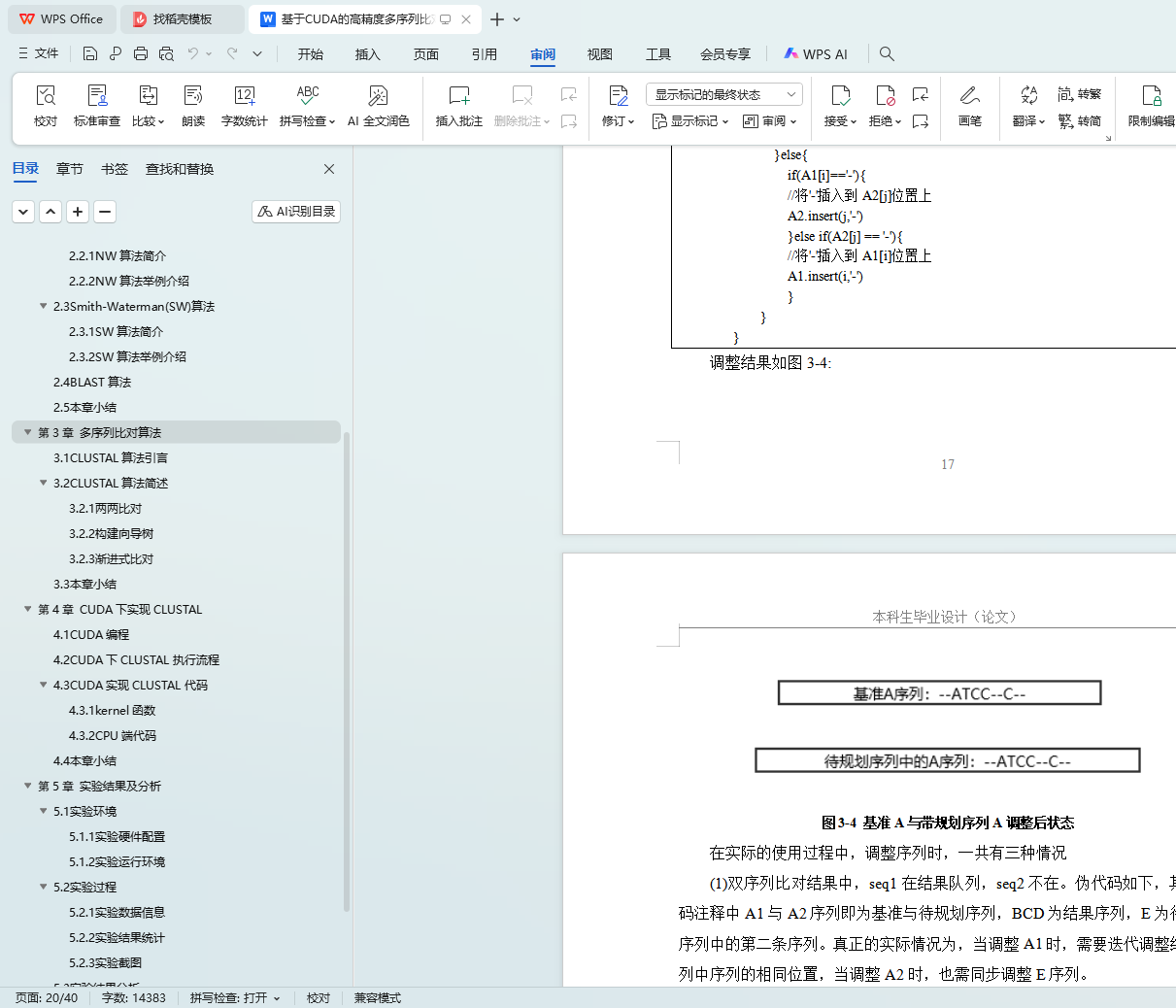
3.2.3 渐进式比对
3.3 本章小结
第4章 CUDA下实现CLUSTAL
4.1 CUDA编程
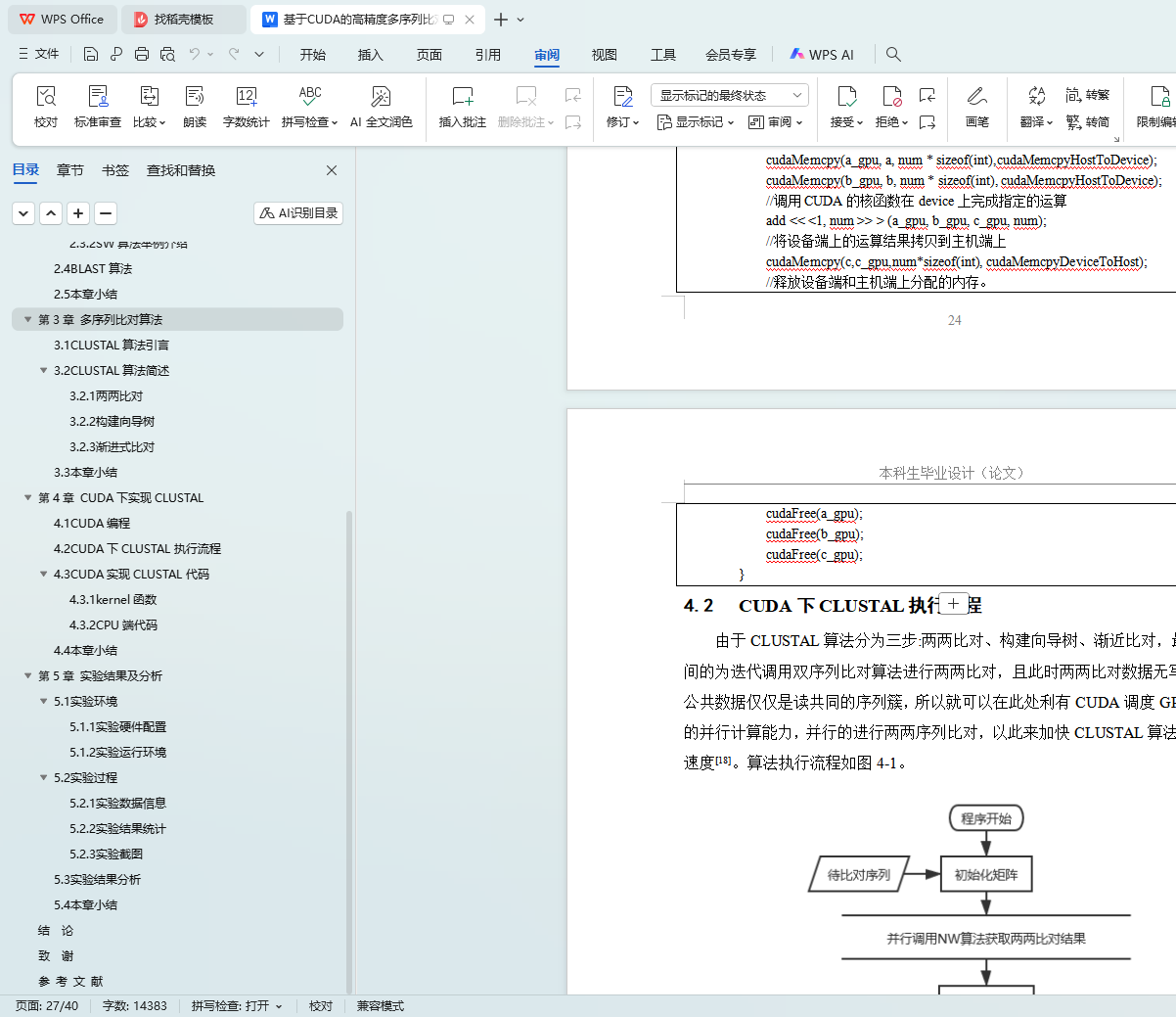
4.2 CUDA下CLUSTAL执行流程
4.3 CUDA实现CLUSTAL代码
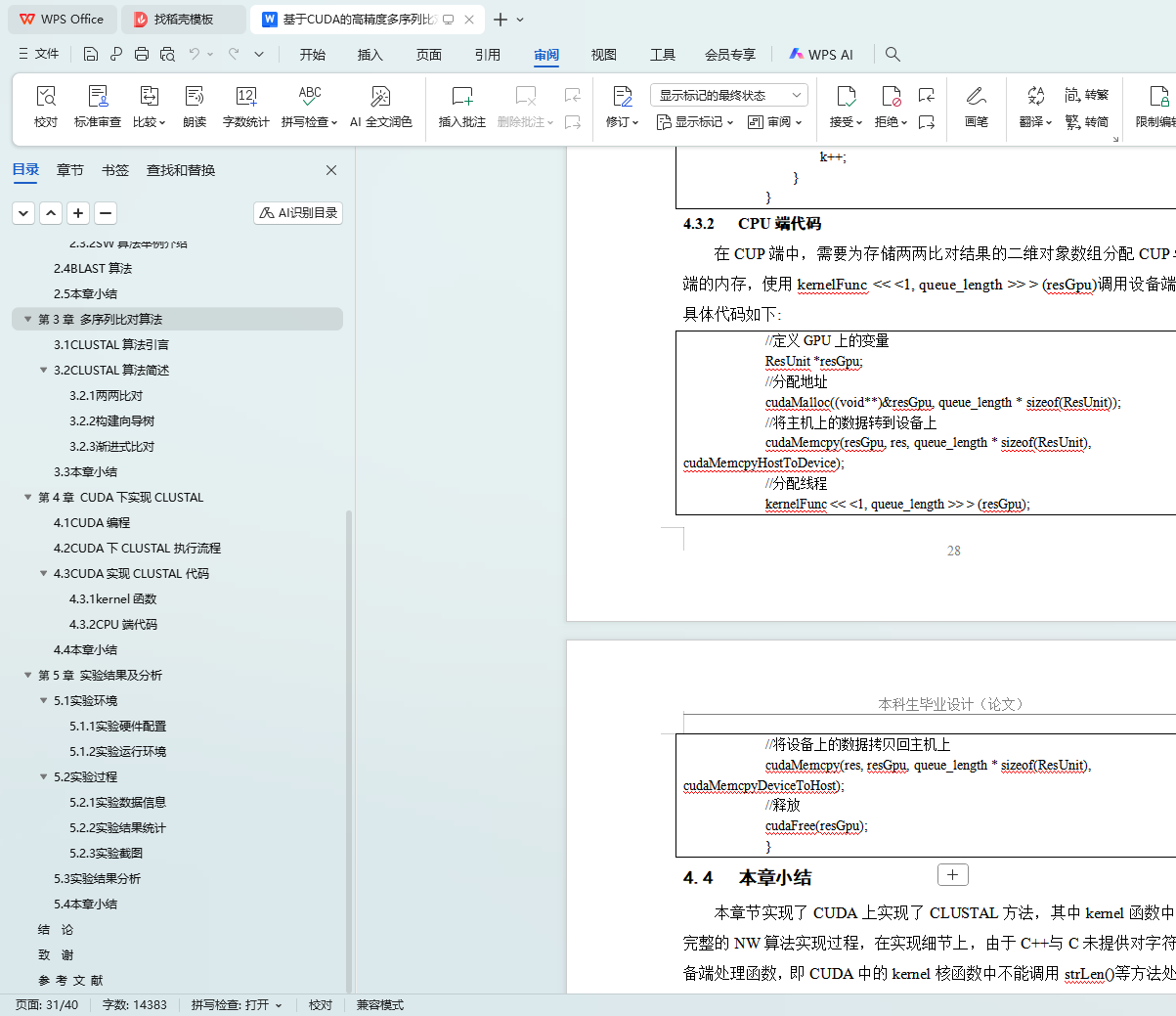
4.3.1 kernel函数
4.3.2 CPU端代码
4.4 本章小结
第5章 实验结果及分析
5.1 实验环境
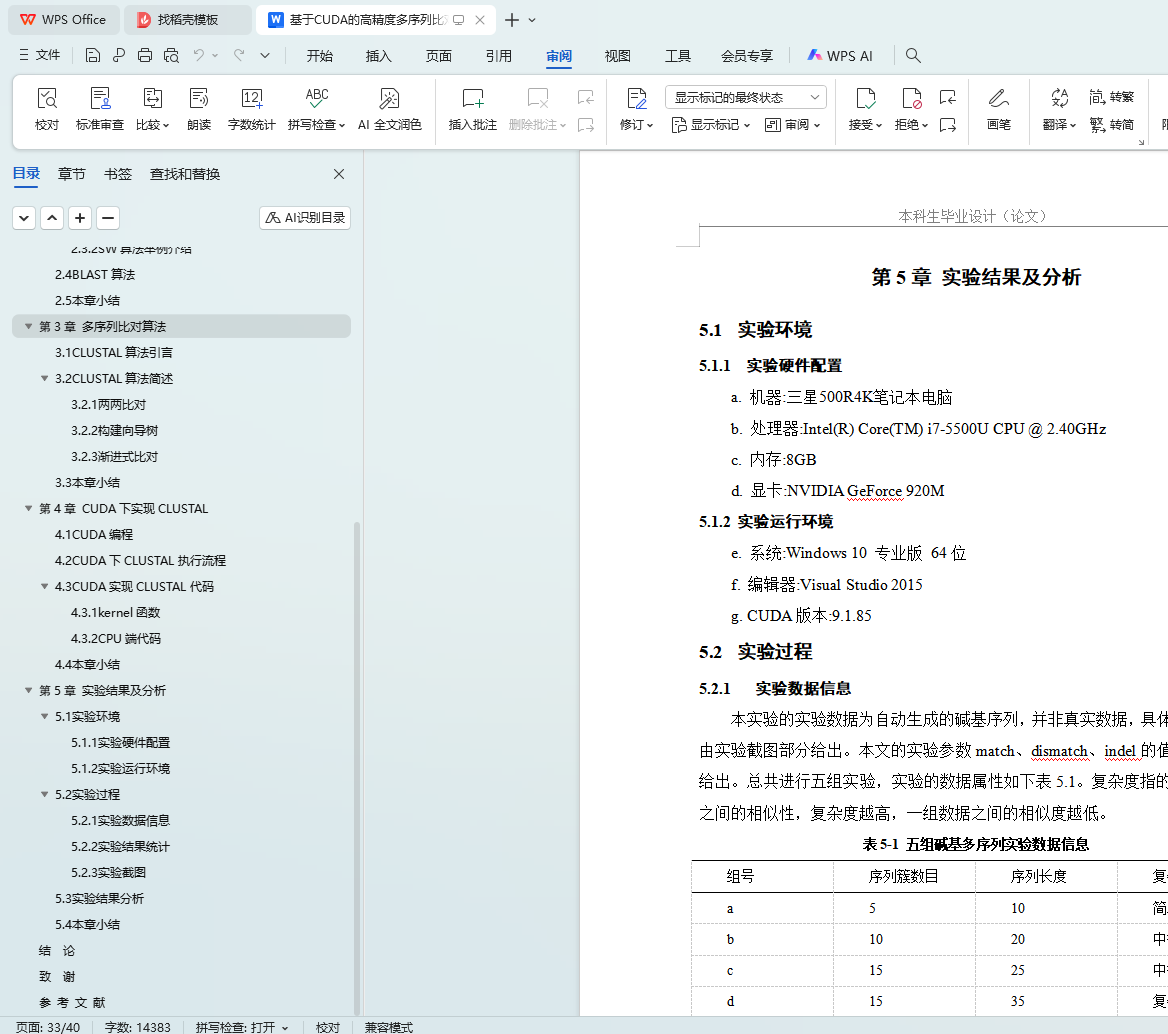
5.1.1 实验硬件配置
5.1.2 实验运行环境
5.2 实验过程
5.2.1 实验数据信息
5.2.2 实验结果统计
5.2.3 实验截图
5.3 实验结果分析
5.4 本章小结
结 论
致 谢
参 考 文 献