摘 要
近年来,智能手机的软硬件都得到大大提升。不断被嵌入手机的各种传感器如加速计、麦克风、GPS等在提供丰富功能的同时,还能收集大量与用户相关的传感器数据。这些数据经过一定的处理和计算,便形成了可以描述用户生活的上下文,例如GPS数据可以推测用户所在的位置,加速计可以感知用户的活动,电话和短信记录反映用户的社交等。由于上下文数据反映了用户的生活状态,如何从用户手机的纵向多源上下文数据中挖掘用户的行为模式,是当前研究的热点和难点。
论文围绕如何从手机上下文中挖掘用户的频繁模式展开研究,首先对传感器数据进行预处理以获得有用的上下文数据,在此基础上,重点研究了纵向多源上下文的处理技术,进而深入研究了在手机上对个体用户频繁模式的挖掘,最后借鉴众包思想,研究了基于云的群体频繁模式挖掘框架。本文的工作主要体现在以下三个方面:
1) 不同于以往对时域数据使用固定时间窗口的方法,针对纵向多源上下文数据的特点以及关联规则挖掘的需要,本文提出了一个动态时间窗口算法来处理上下文数据,具体地讲,首先根据用户的交互活动(包括电话、短信、应用软件的使用记录)动态确定时间窗口,
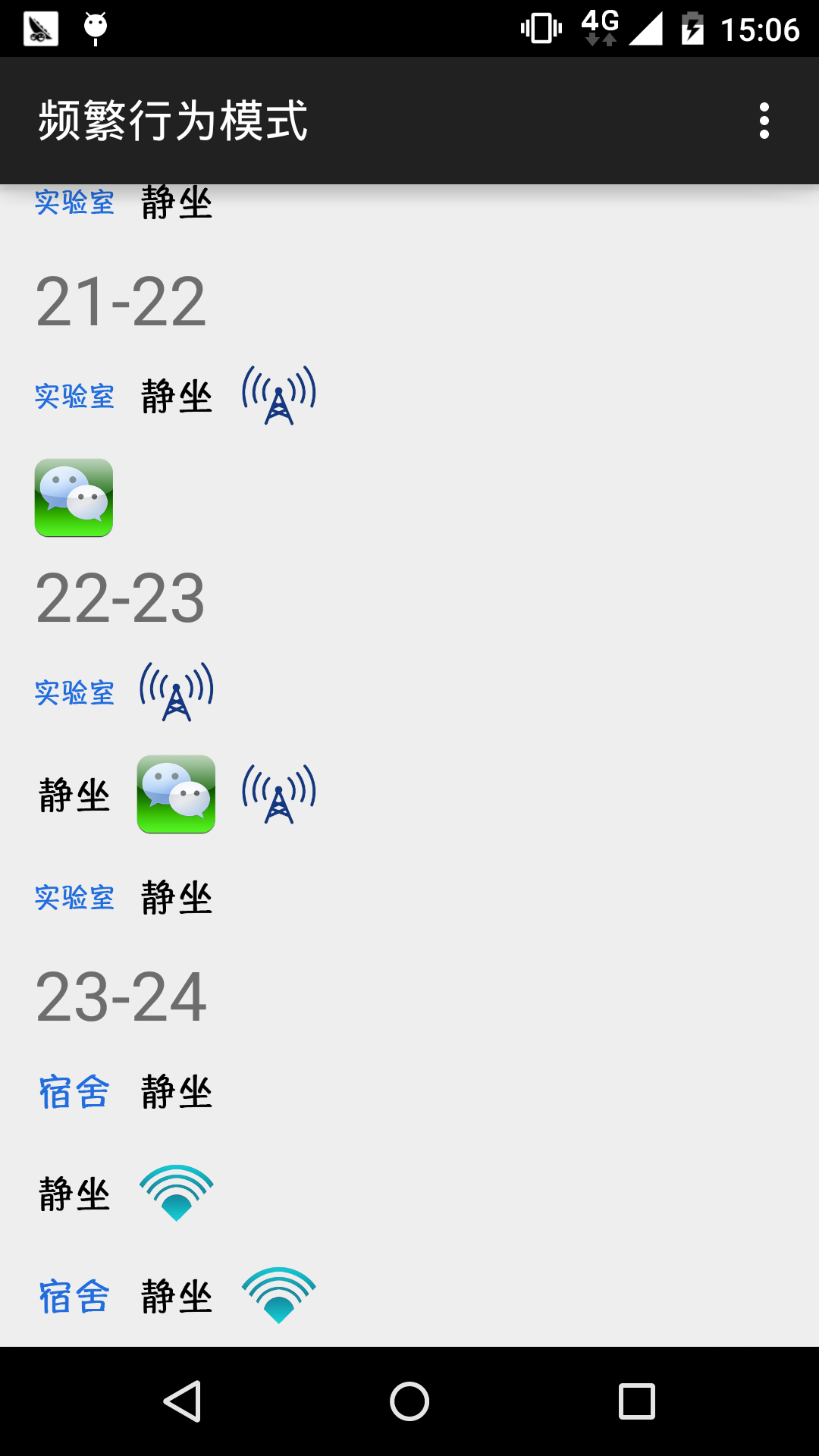
2) 为了实现在手机上对个体用户频繁模式的挖掘,考虑手机处理能力的限制,本文提出了一个频繁模式挖掘模型,通过对频繁模式的分析定义,确定了两个关键的因素,即用户交互活动的持续时间和出现频率,然后基于传统的Apriori挖掘算法,在支持度的定义上对上述两个因素进行加权,从而获得更加客观准确的频繁模式。此外,挖掘模型还对挖掘结果进行进一步的可视化处理,对用户在不同地方和不同时段的行为模式进行展示,方便用户随时了解自己的日常行为模式。
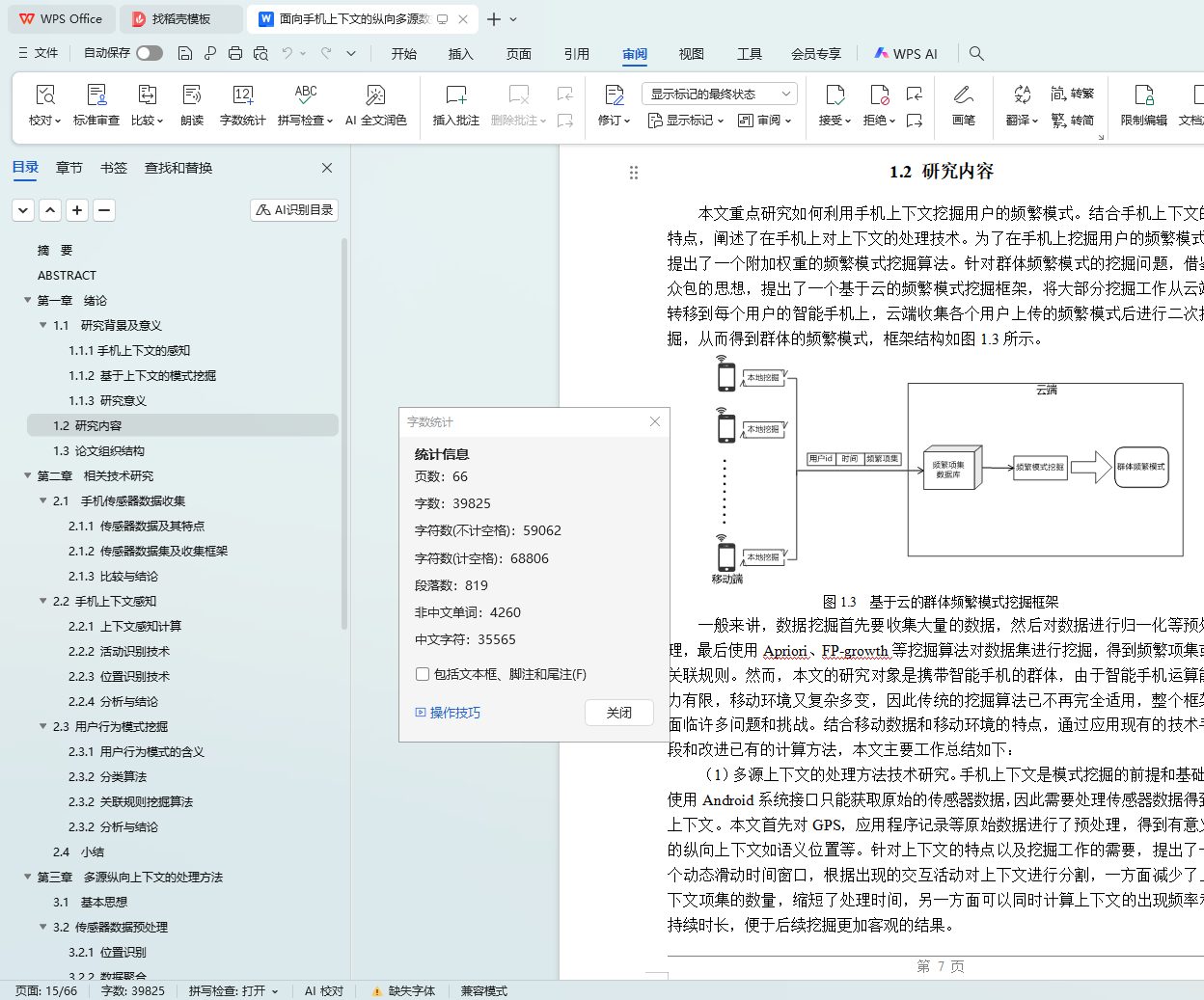
3) 在上述研究基础上,针对群体频繁模式的挖掘问题,本文设计实现了一个基于云的挖掘系统,对用户上传的频繁模式汇总后进行二次挖掘。由于不同用户频繁模式的差异,为保证结果能反映群体的特征,本文扩展了Apriori挖掘算法,使用用户频繁模式的支持度和比重作为一个附加权重。云框架使用了百度云应用引擎进行实现,通过实验验证了算法及框架的可靠性和实用性。
主题词:移动数据;手机上下文;滑动窗口;模式挖掘;数据挖掘;
ABSTRACT
In recent years, the hardware and software of smartphones have been greatly enhanced. Various sensors such as accelerometers, microphones, GPS and so on continue to be embedded in the smartphones, which not only provide rich functions, but also collect a large number of sensors data relevant to the user. After processing these data, context data which can describe the life of user is generated. For example, GPS data can be used to speculate user's location, and the accelerometer date can be used to sense user's activities. What’s more, the records of calls and SMS can reflect user's social contact. Since contextual data can reflect the user's living conditions, how to mine user’s behavior patterns from the longitudinal multi-source contextual data of user is the current hot and difficult research problem.
Concentrating on how to mine user’s frequent patterns from mobile contextual data, firstly, we preprocess the sensor data to obtain useful contextual data. Secondly, we focus on the processing technology of longitudinal multi-source contextual data and then study how to mine user’s frequent patterns on smartphones deeply. Finally, we study cloud-based community frequent patterns mining framework. Work in this paper is mainly reflected in the following three aspects:
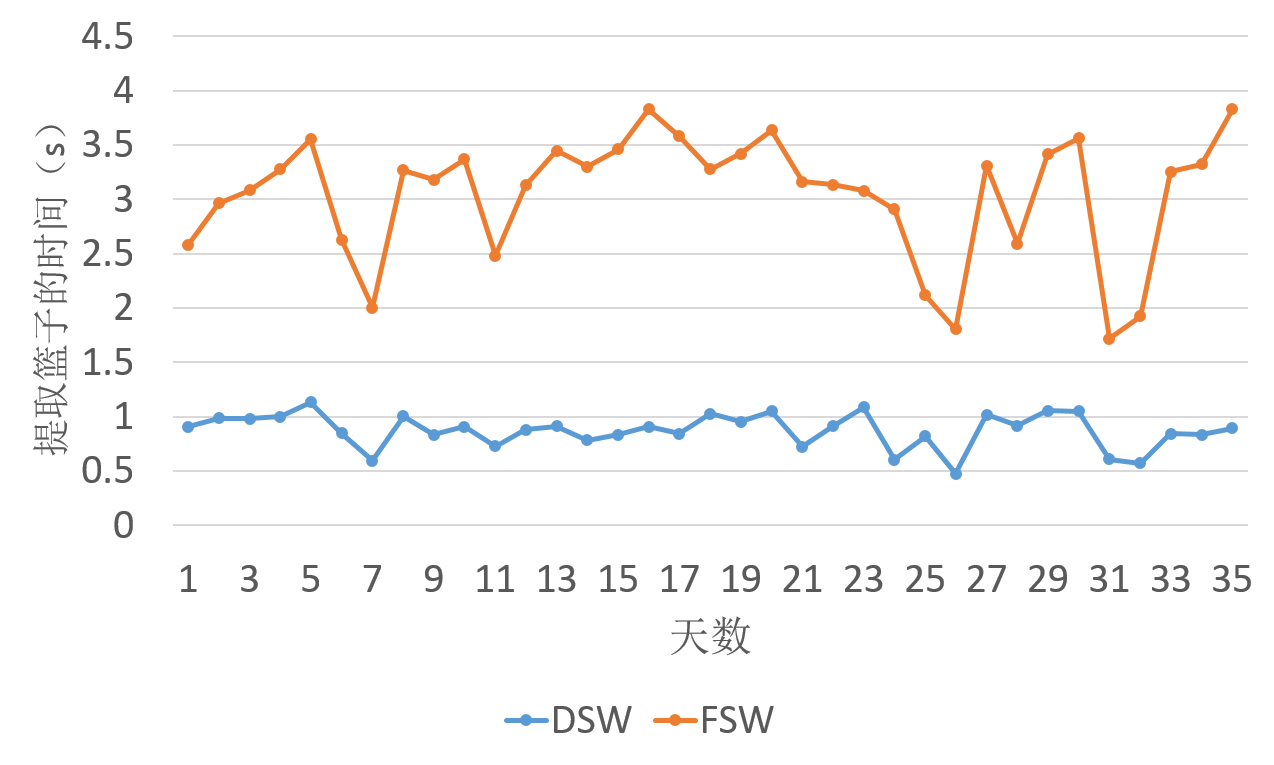
(1) Unlike the previous method of fixed time window, considering the characteristics of longitudinal multi-source context data and the need for mining association rules, this paper presents a dynamic time window algorithm to process context data. Specifically, the length of time window is determined dynamically based on user’s interaction (including calling, texting, and running application). Then each context data is divided by the time window into context item sets. We proved that this method is superior to other methods in experiments.
(2) In order to mine individual frequent pattern on the smartphone, considering the limited processing capacity of the smartphone, this paper presents a frequent pattern mining model. By analyzing the definition of frequent pattern, we identified two key factors, namely the duration and frequency of user’s interaction. Then we add the two factors to the definition of support in Apriori algorithm to obtain more accurate frequent patterns. In addition, we visualize the mining results and display them in different places and at different times, which is easy for users to understand their own everyday behavior patterns.
(3) Based on the above research, focusing on the community frequent pattern mining, we design and implement a cloud-based pattern mining framework which aggregates and mines uploaded frequent patterns by users. Due to differences in frequent patterns of users, in order to ensure the results can reflect the characteristics of community, this paper extends the mining algorithm Apriori and takes support and proportion of frequent pattern as an additional weight. Cloud framework are implemented based on Baidu cloud engine. We verify the reliability of the algorithm and practicality of the frame experimentally.
Key Words:Mobile Data; Mobile Context; Sliding Window; Pattern Mining; Data Mining;
目 录
摘 要
ABSTRACT
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景及意义
1.1.1手机上下文的感知
1.1.2 基于上下文的模式挖掘
1.1.3 研究意义
1.2 研究内容
1.3 论文组织结构
第二章 相关技术研究
2.1 手机传感器数据收集
2.1.1 传感器数据及其特点
2.1.2 传感器数据集及收集框架
2.1.3 比较与结论
2.2 手机上下文感知
2.2.1 上下文感知计算
2.2.2 活动识别技术
2.2.3 位置识别技术
2.2.4 分析与结论
2.3 用户行为模式挖掘
2.3.1 用户行为模式的含义
2.3.2 分类算法
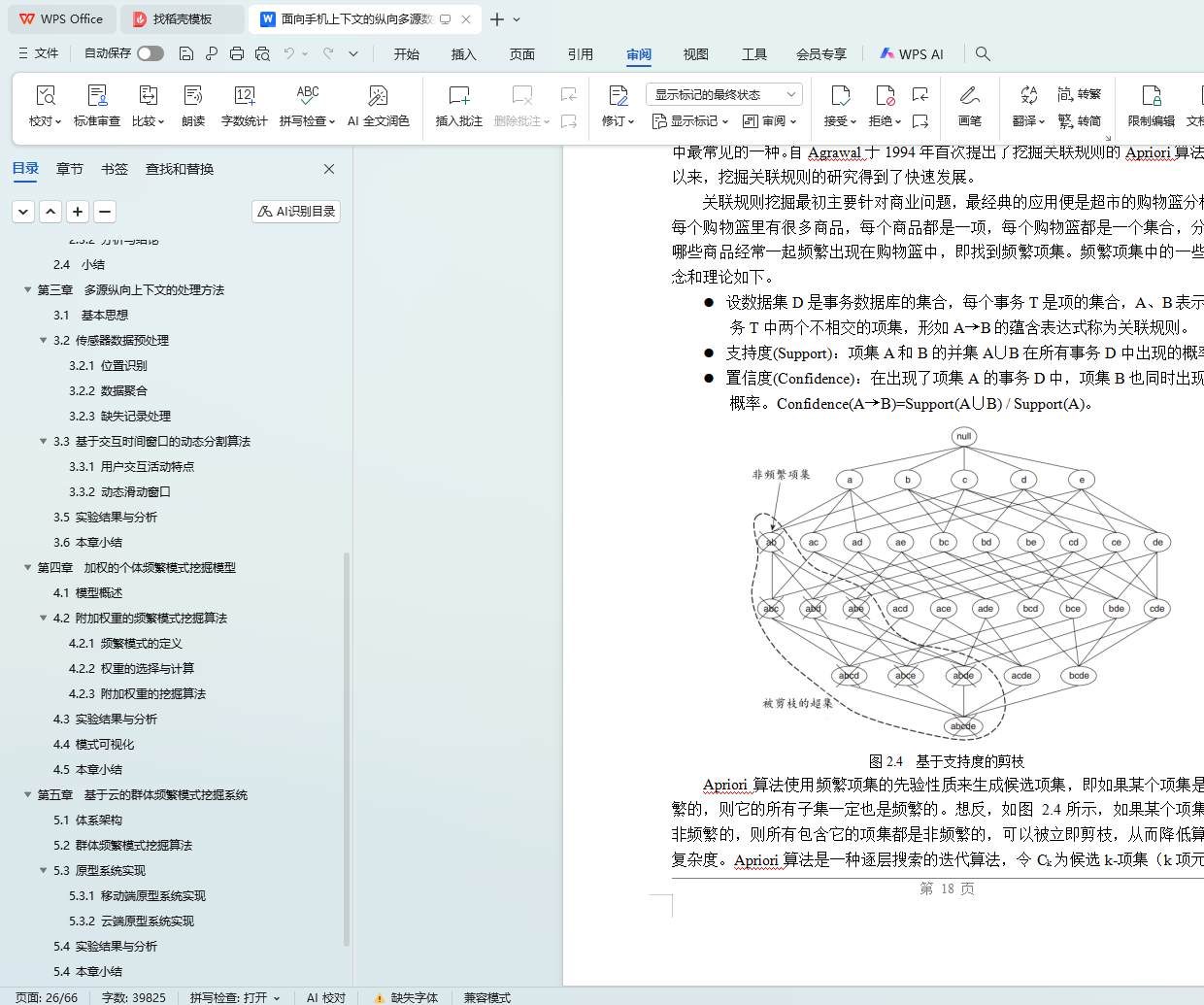
2.3.2 关联规则挖掘算法
2.3.2 分析与结论
2.4 小结
第三章 多源纵向上下文的处理方法
3.1 基本思想
3.2 传感器数据预处理
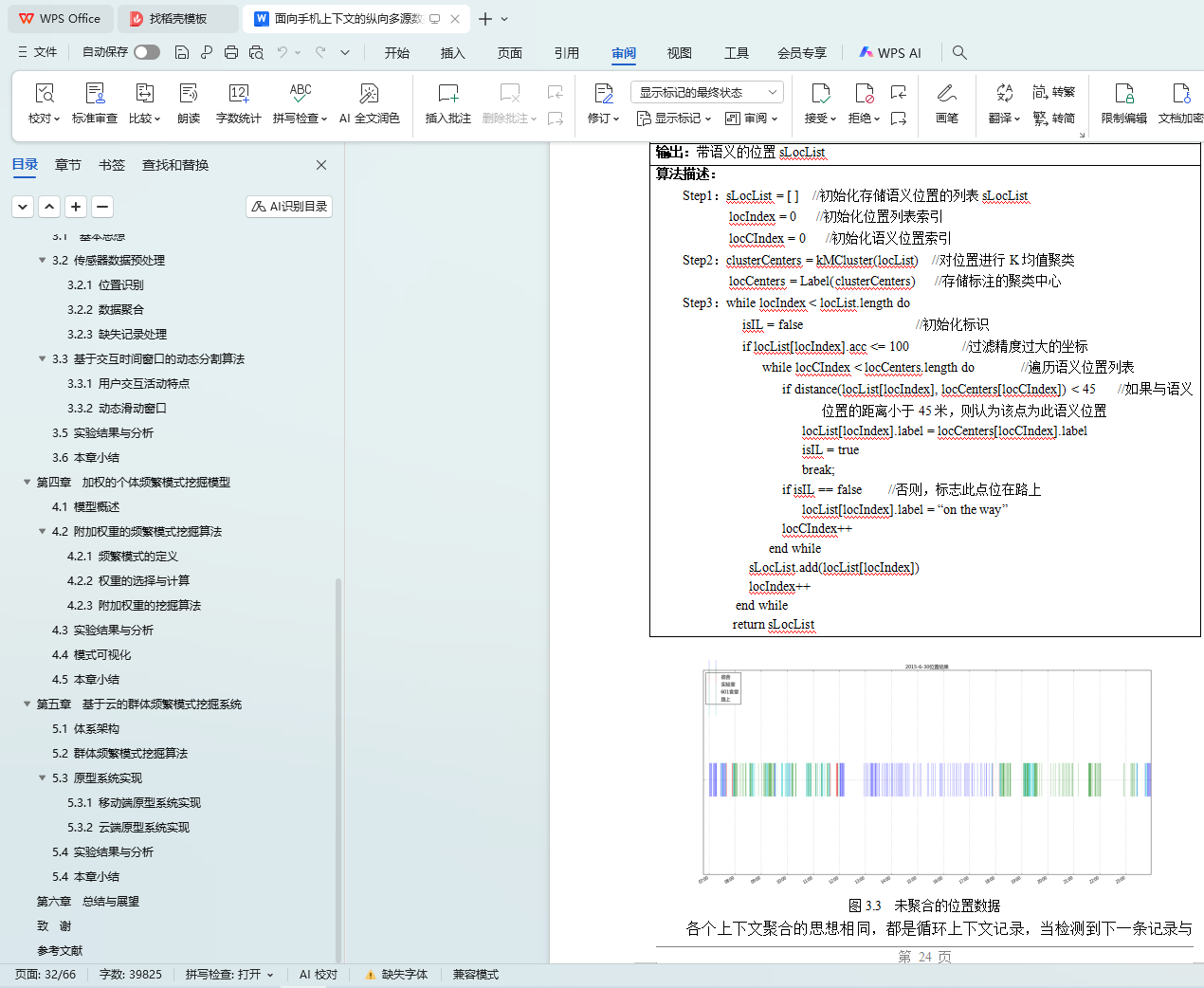
3.2.1 位置识别
3.2.2 数据聚合
3.2.3 缺失记录处理
3.3 基于交互时间窗口的动态分割算法
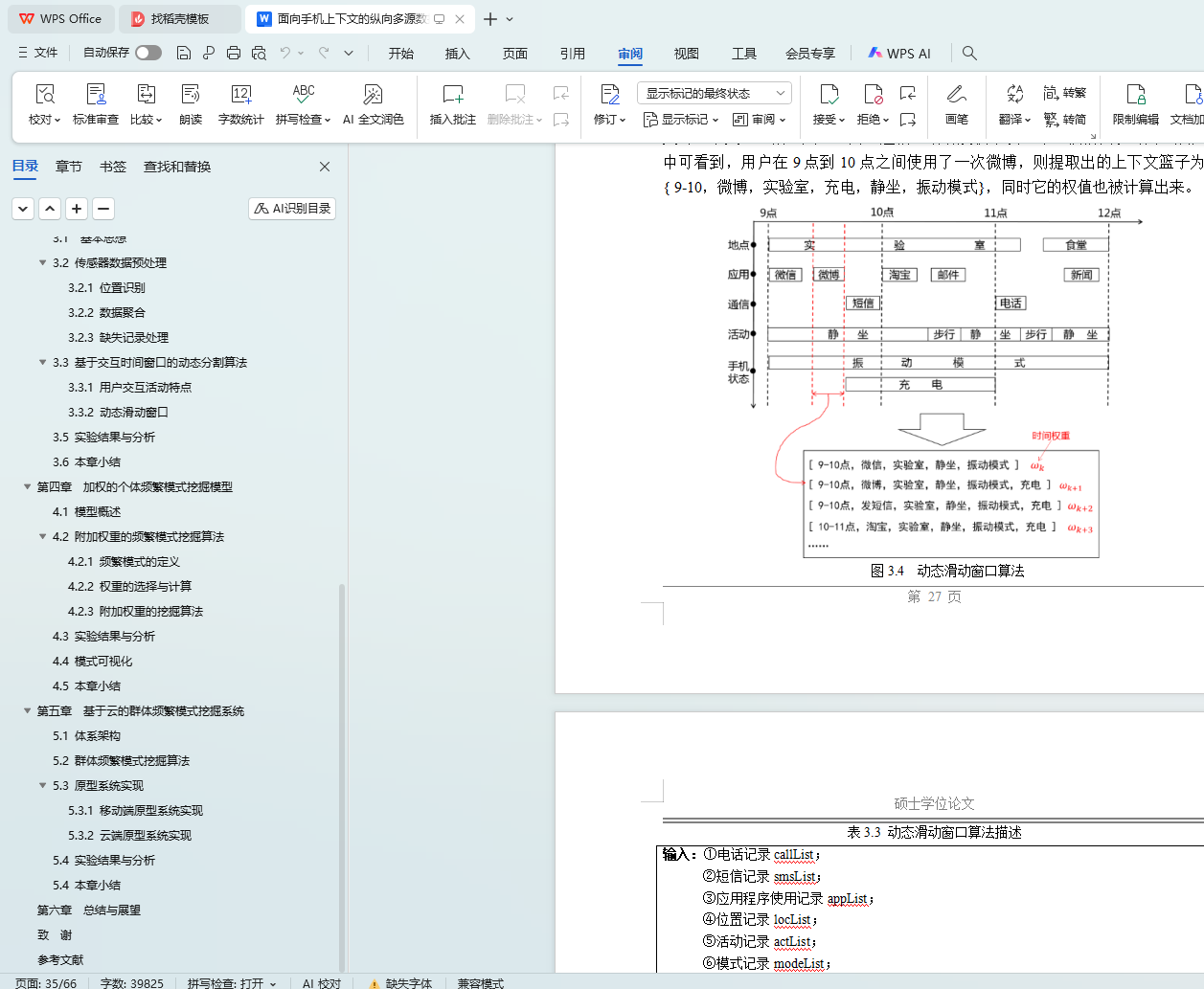
3.3.1 用户交互活动特点
3.3.2 动态滑动窗口
3.5 实验结果与分析
3.6 本章小结
第四章 加权的个体频繁模式挖掘模型
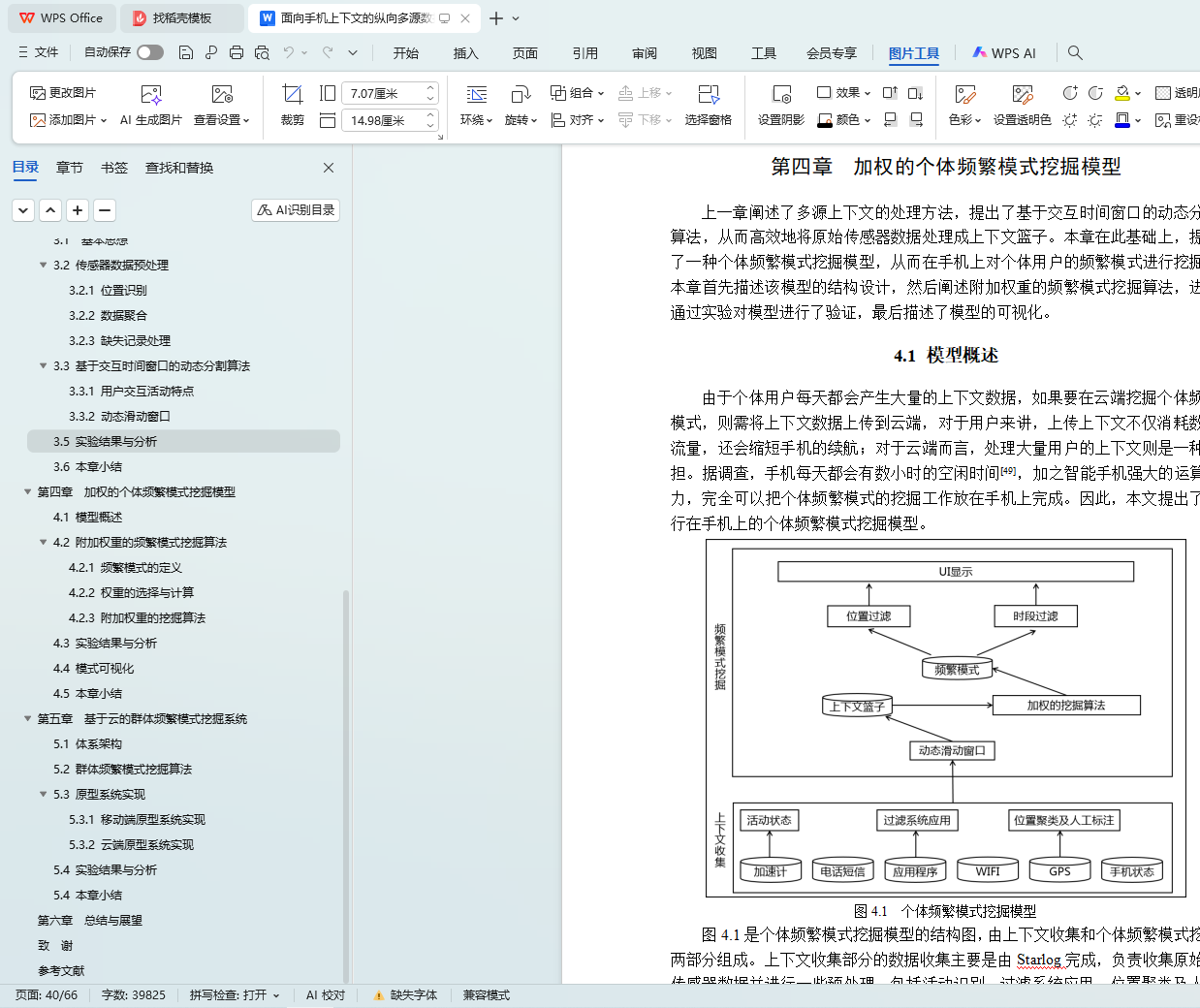
4.1 模型概述
4.2 附加权重的频繁模式挖掘算法
4.2.1 频繁模式的定义
4.2.2 权重的选择与计算
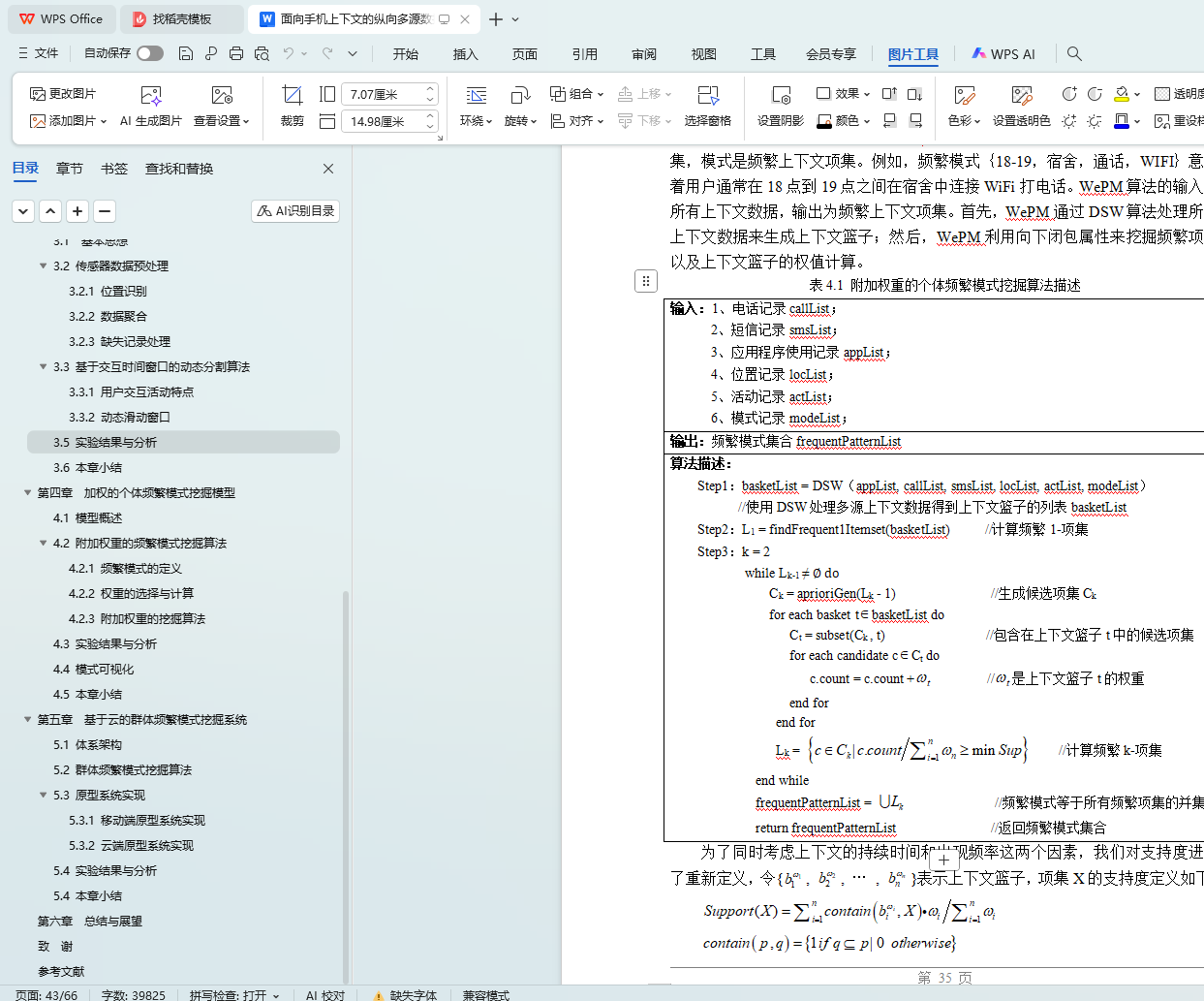
4.2.3 附加权重的挖掘算法
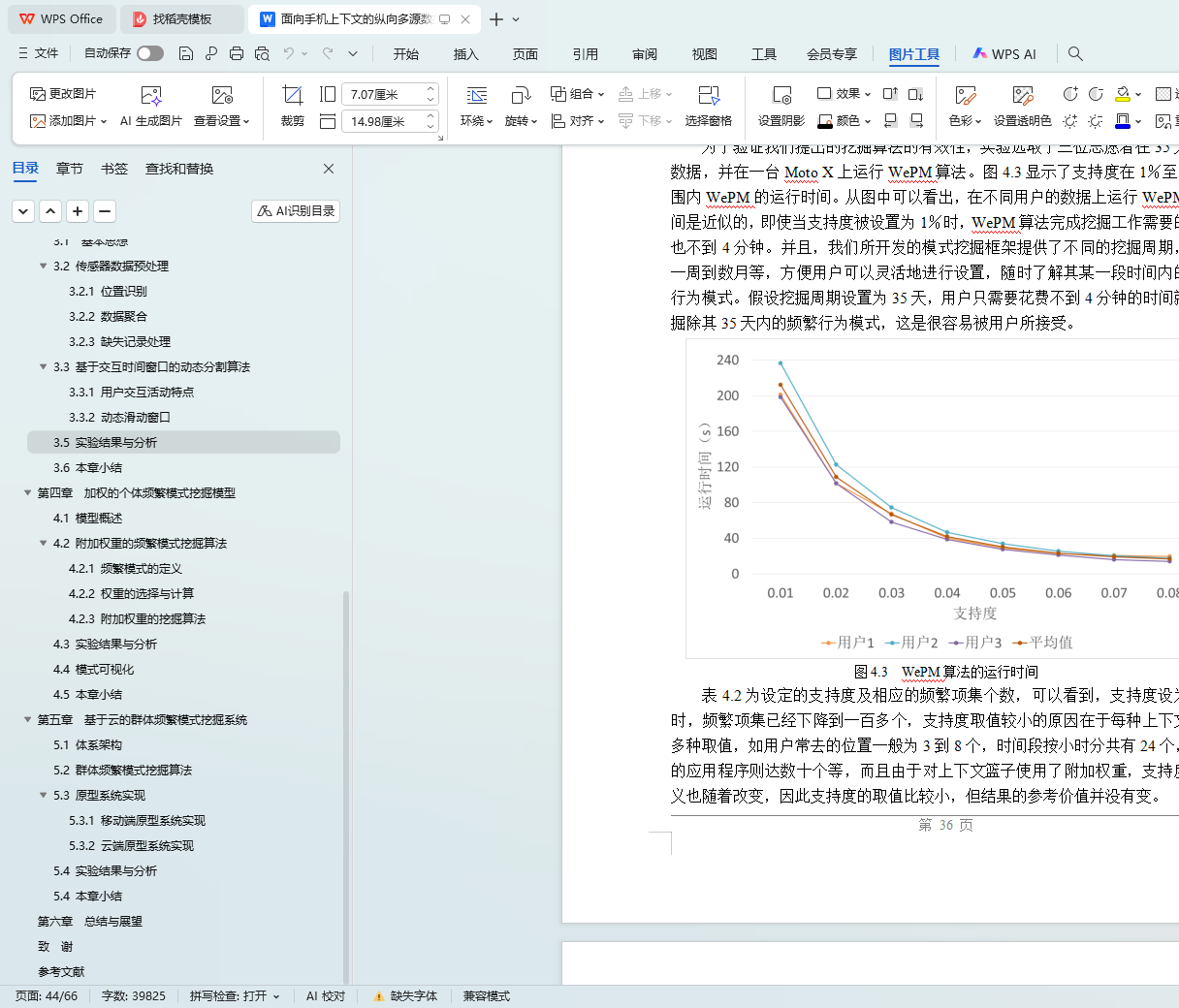
4.3 实验结果与分析
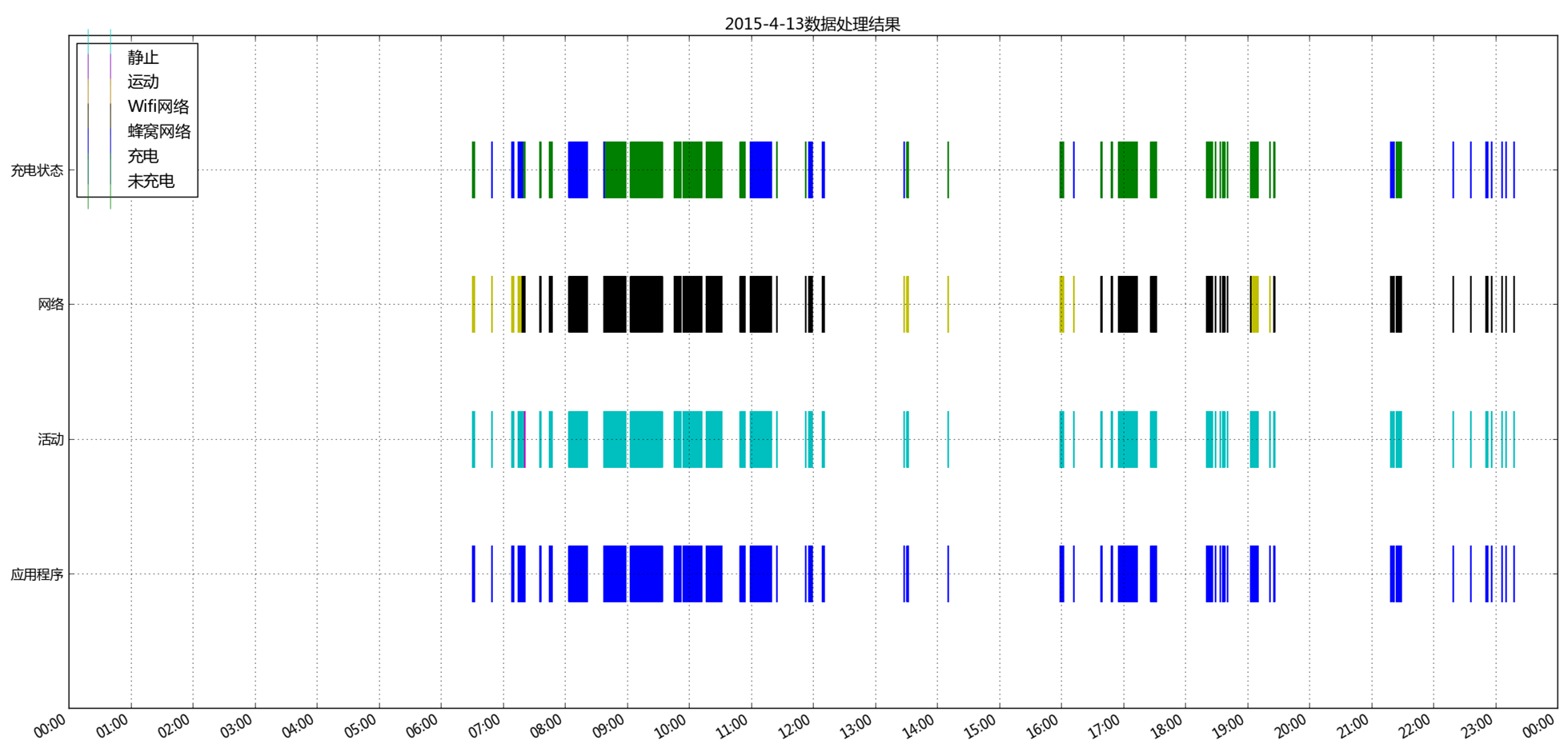
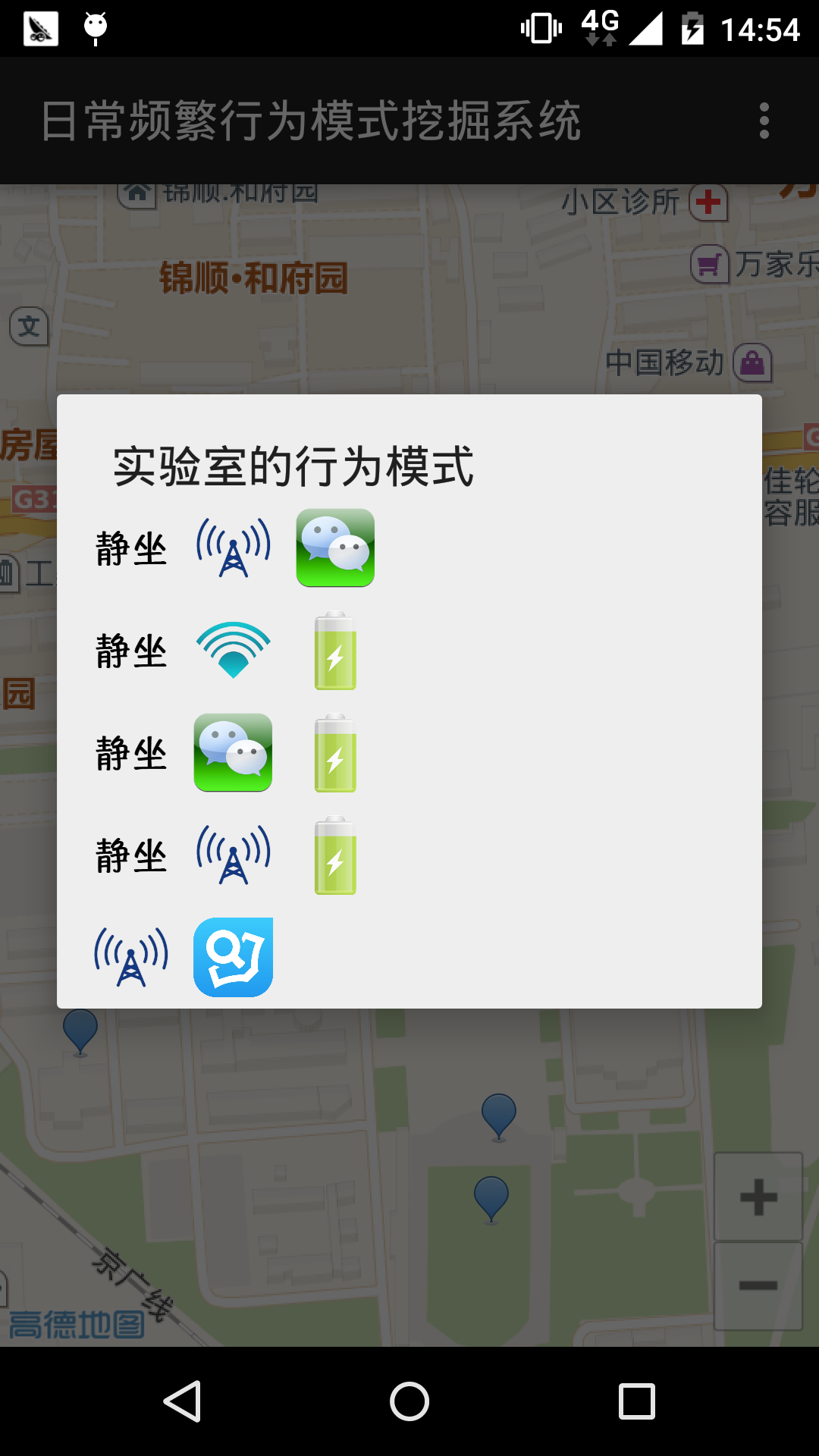
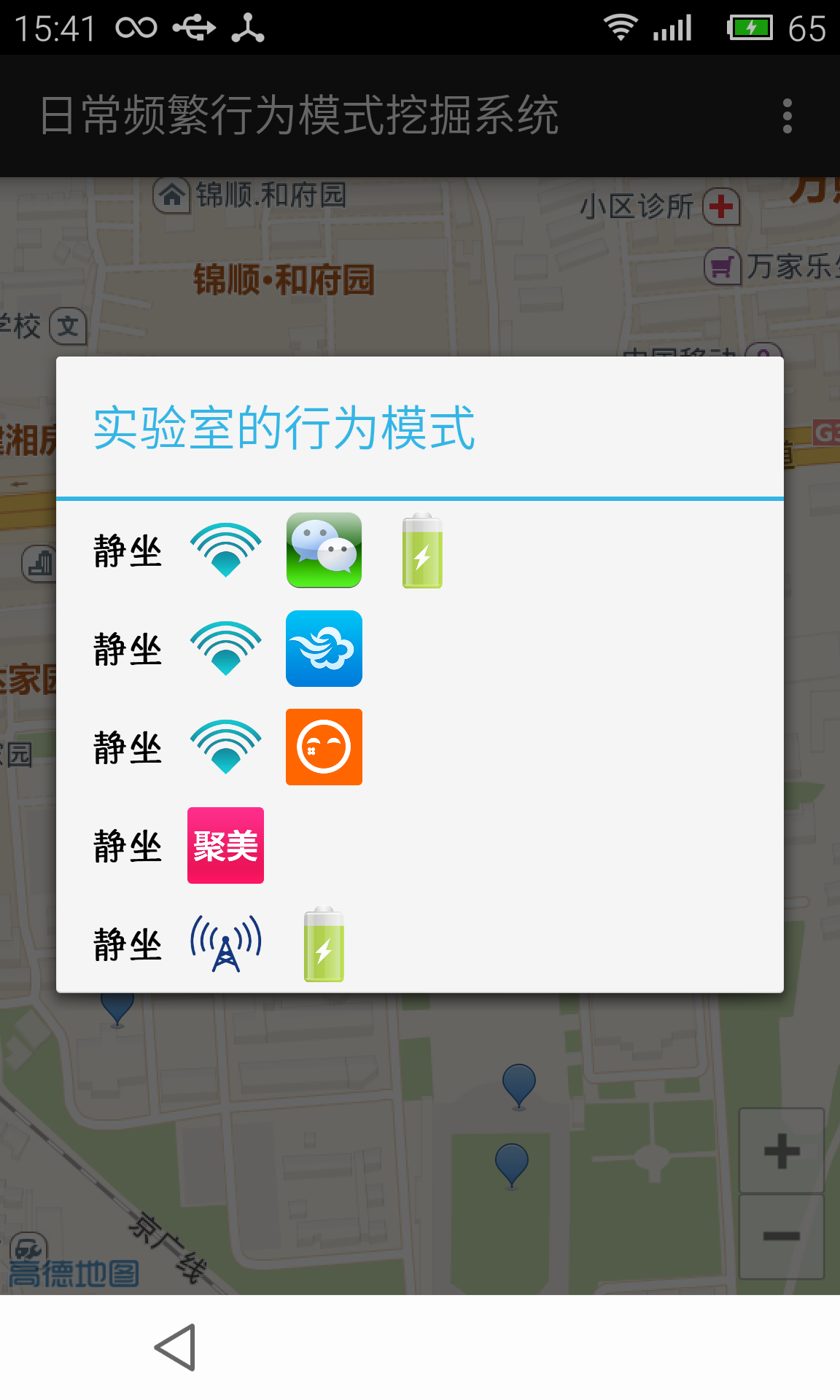
4.4 模式可视化
4.5 本章小结
第五章 基于云的群体频繁模式挖掘系统
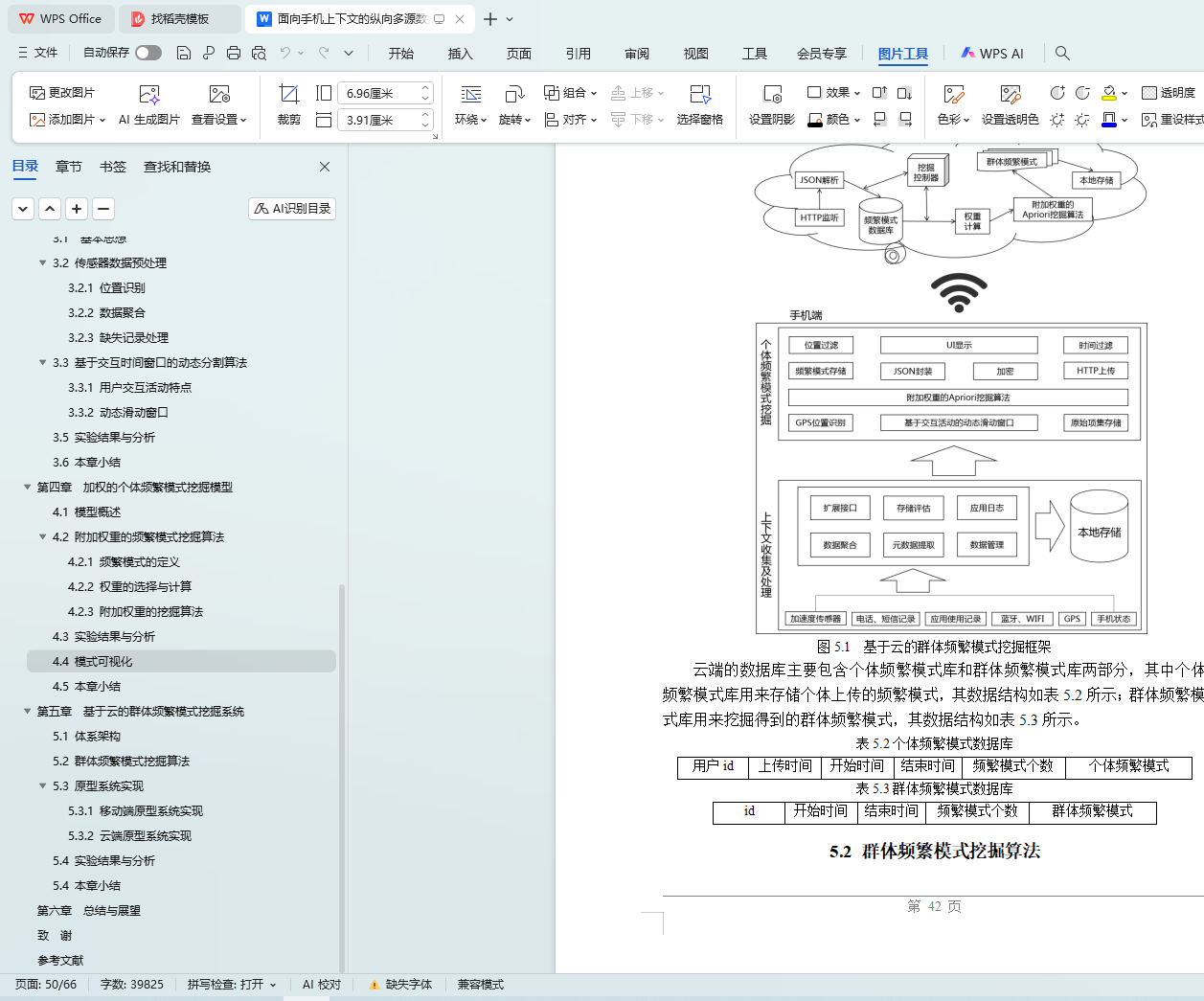
5.1 体系架构
5.2 群体频繁模式挖掘算法
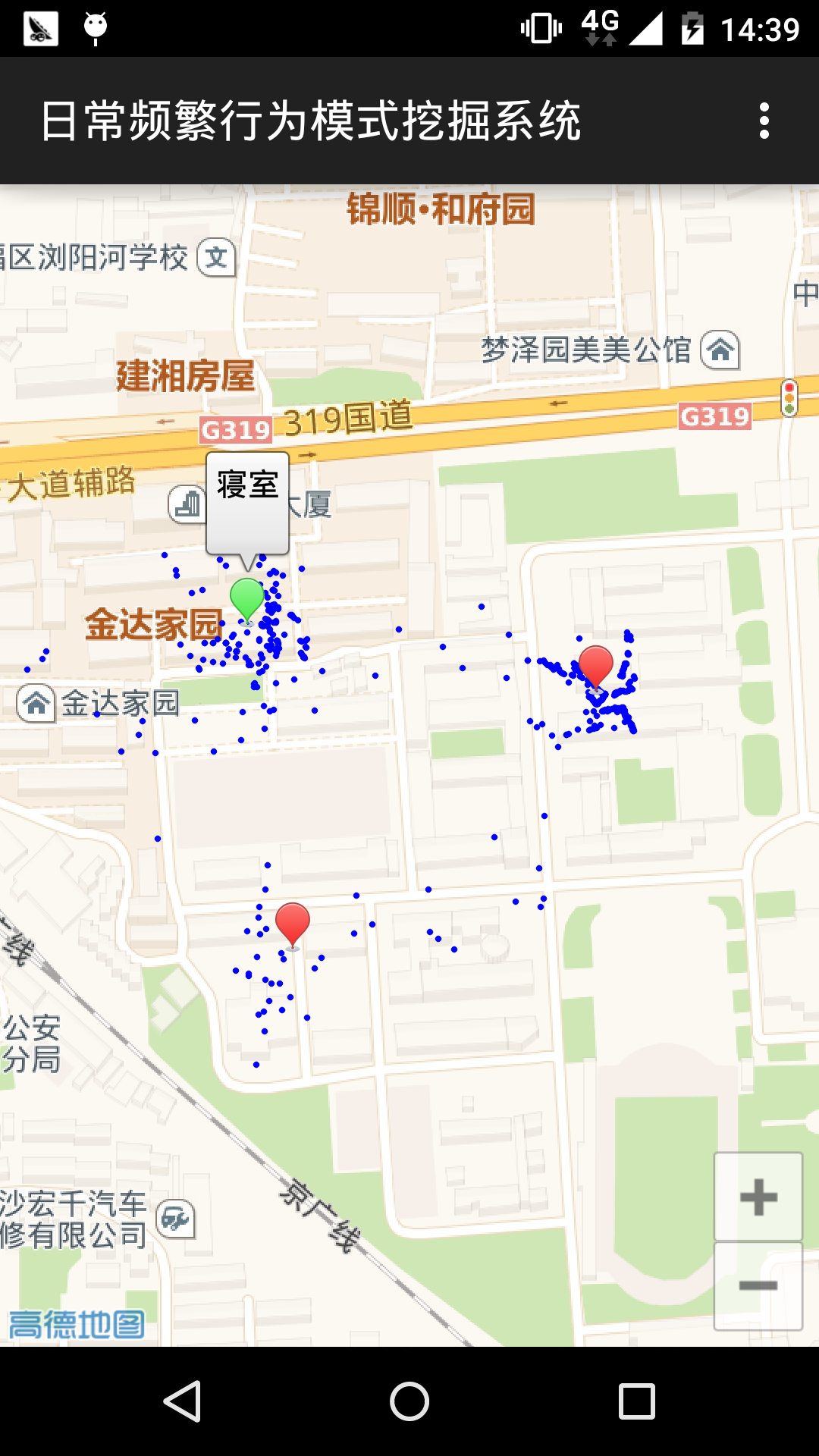
5.3 原型系统实现
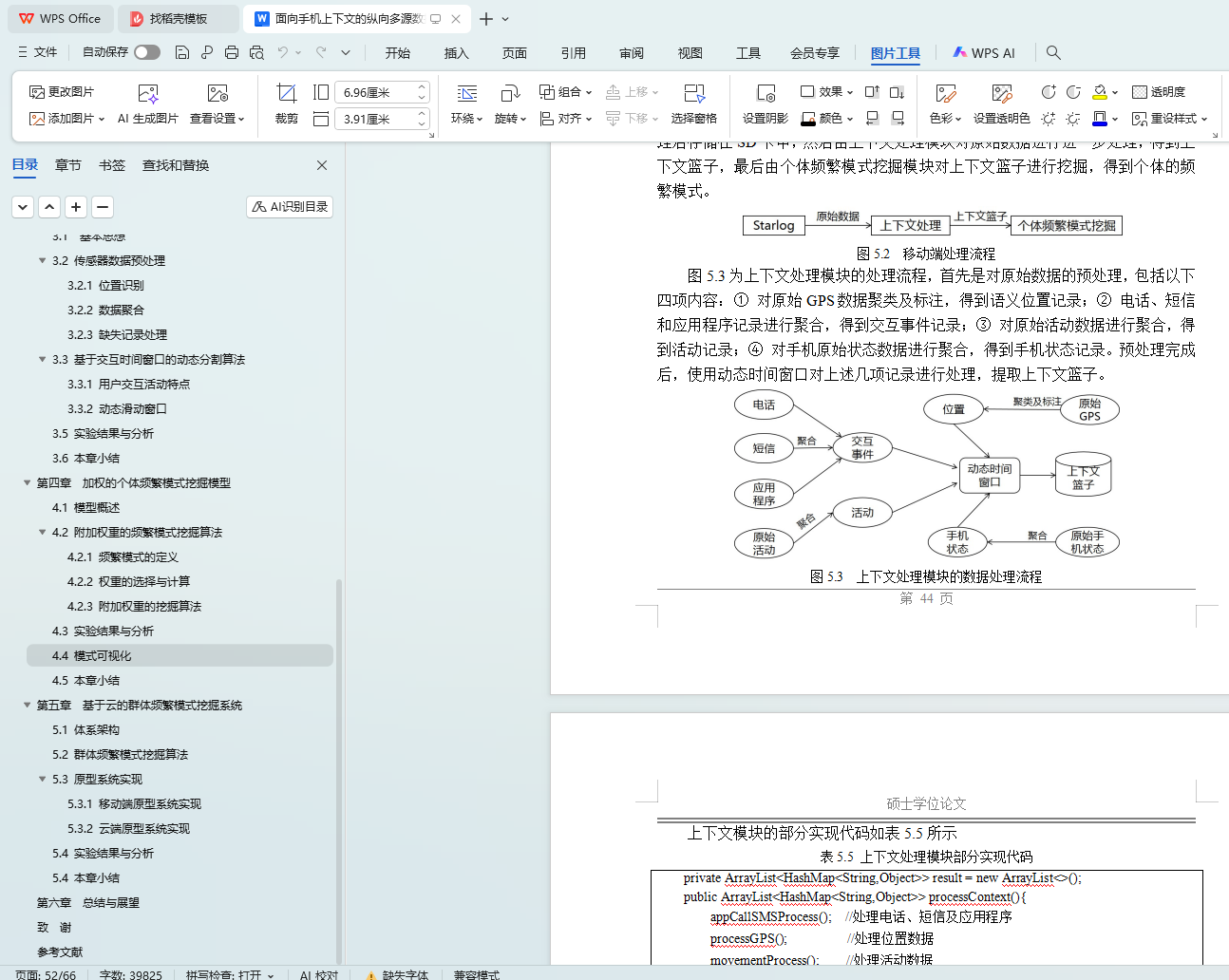
5.3.1 移动端原型系统实现
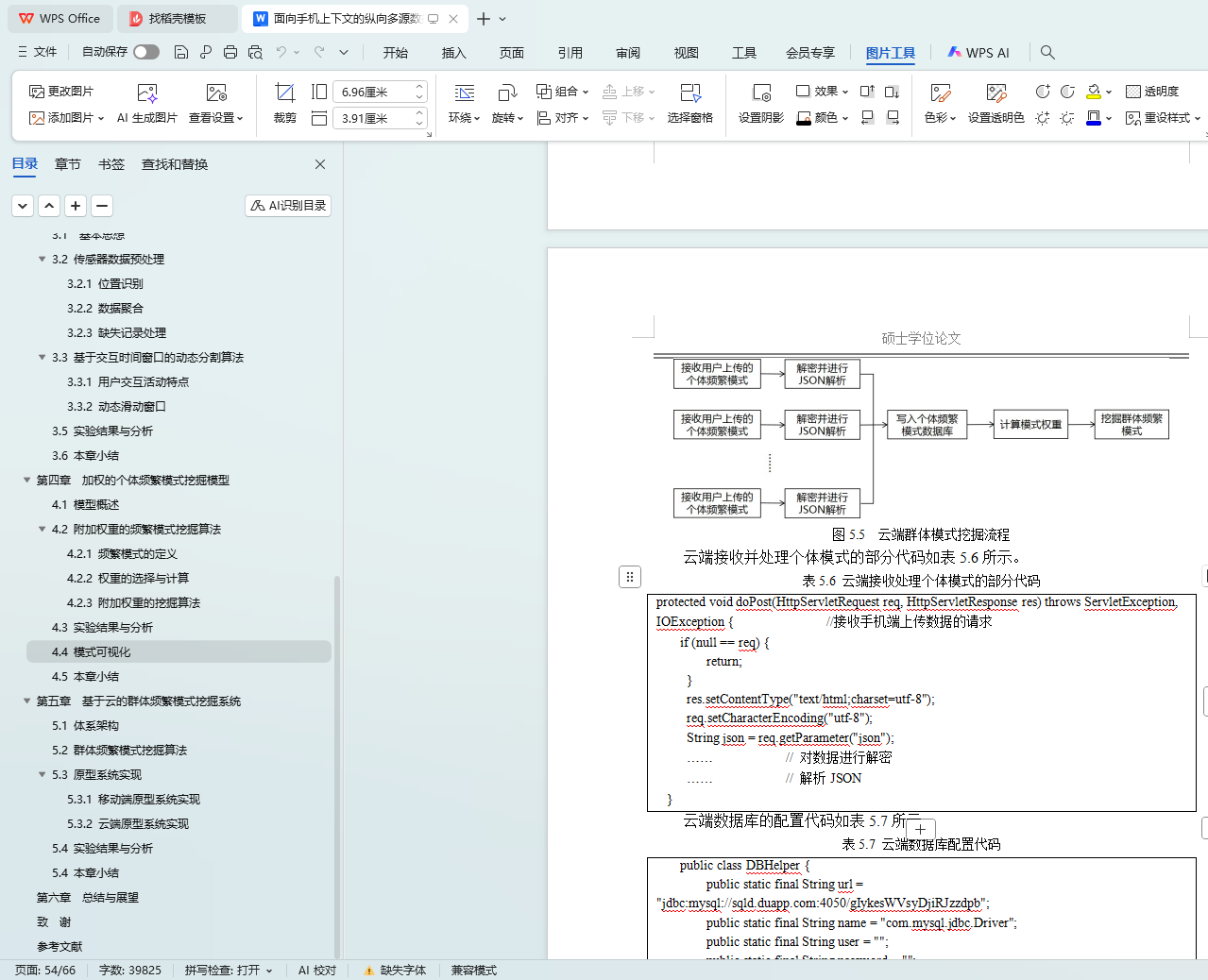
5.3.2 云端原型系统实现
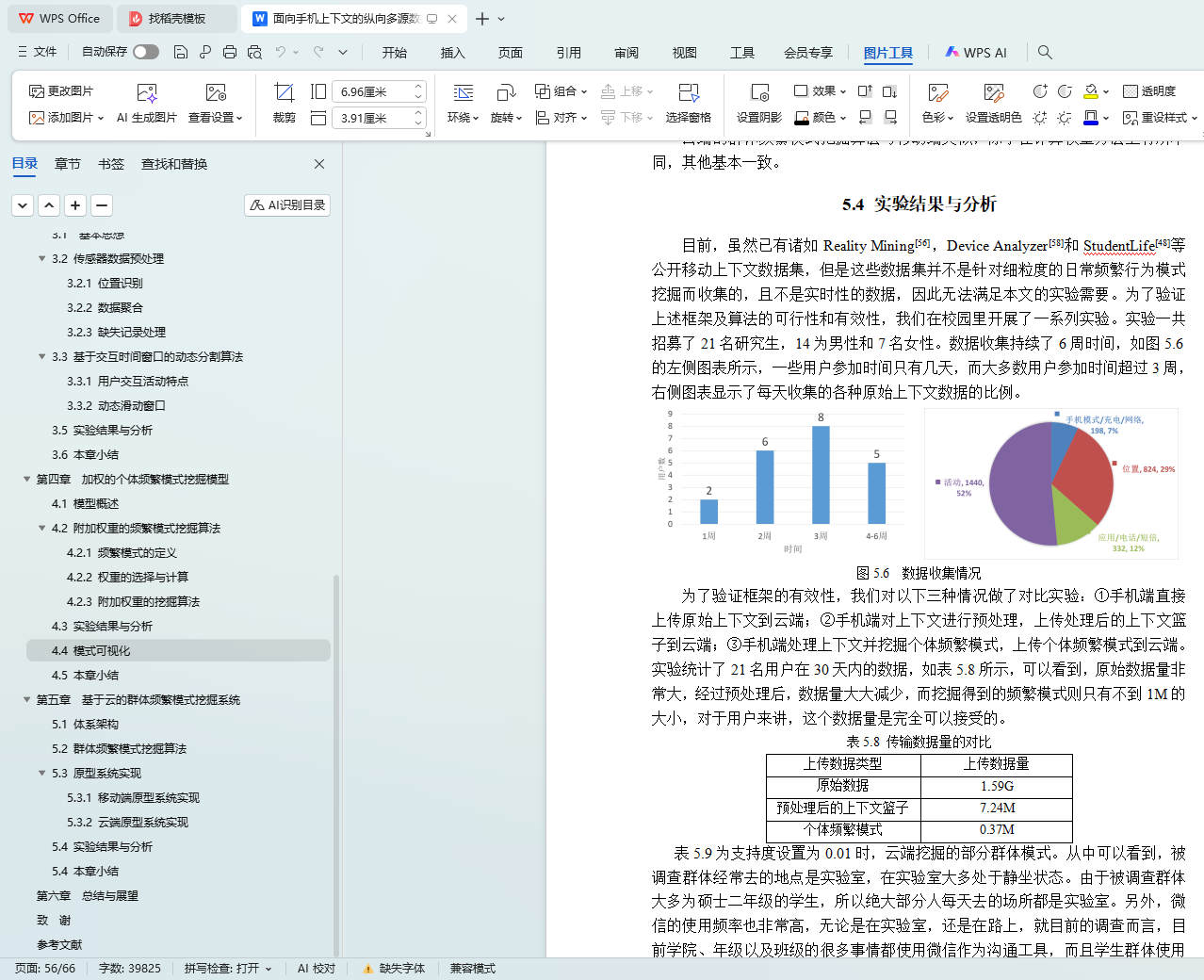
5.4 实验结果与分析
5.4 本章小结
第六章 总结与展望
致 谢
参考文献