摘 要
知识图谱是一种将知识进行结构化存储的技术,被广泛应用于自然语言处理、推荐系统、信息检索等多个领域。本文研究的实体链接,任务目标是找到文本中已识别的指称与目标知识图谱中实体之间语义一致的映射,从而消除自然语言表达的多样性和歧义性,是知识图谱构建和应用过程中的关键环节。实体链接通常分为候选实体召回和候选实体排序两个阶段。候选实体召回常用的方法依赖于实体别名列表,而别名列表的构建和优化需要耗费大量的人力和时间,且难以在不同领域之间迁移。而对于候选实体排序,现有的方法存在如下问题:1). 基于预训练模型的候选实体排序方法,使用的预训练任务与实体链接任务之间存在差异,无法准确学习指称特征与实体特征之间关联;2). 基于图表示的候选实体排序方法,未能准确地对文档中的文本、指称以及候选实体之间关系进行建模。本文针对这些问题和挑战进行了以下研究:
(1) 候选实体召回方法研究。针对候选实体名称的多样性,分别对基于字符串匹配的方法和基于语义向量检索的方法进行研究。候选实体一些名称通常都具有相同的前缀或后缀,根据这一特点,本文提出使用字典树构建实体别名索引进行前后缀匹配的方法,以较少的额外计算代价取得召回率的提升。本文提出基于预训练模型对实体进行语义编码,然后通过语义向量近似检索完成候选实体召回的方法。实验表明,实体缺少别名列表时使用语义向量检索作为字符串匹配方法的补充可以进一步提升候选实体召回的效果。
(2) 基于自监督学习的候选实体排序方法研究。在候选实体排序阶段,现有方法使用预训练模型学习指称上下文和候选实体特征之间的语义关联,而预训练任务与实体链接任务存在明显差异;为了消除这种差异的影响,本文提出基于自监督学习的候选实体排序方法,利用现有的知识图谱构建实体链接相关的判别式自监督学习任务。此外,使用对抗训练及多任务学习等方法进一步提升模型的泛化性。实验表明该方法能提升实体链接的准确率,且训练数据越少提升越明显。
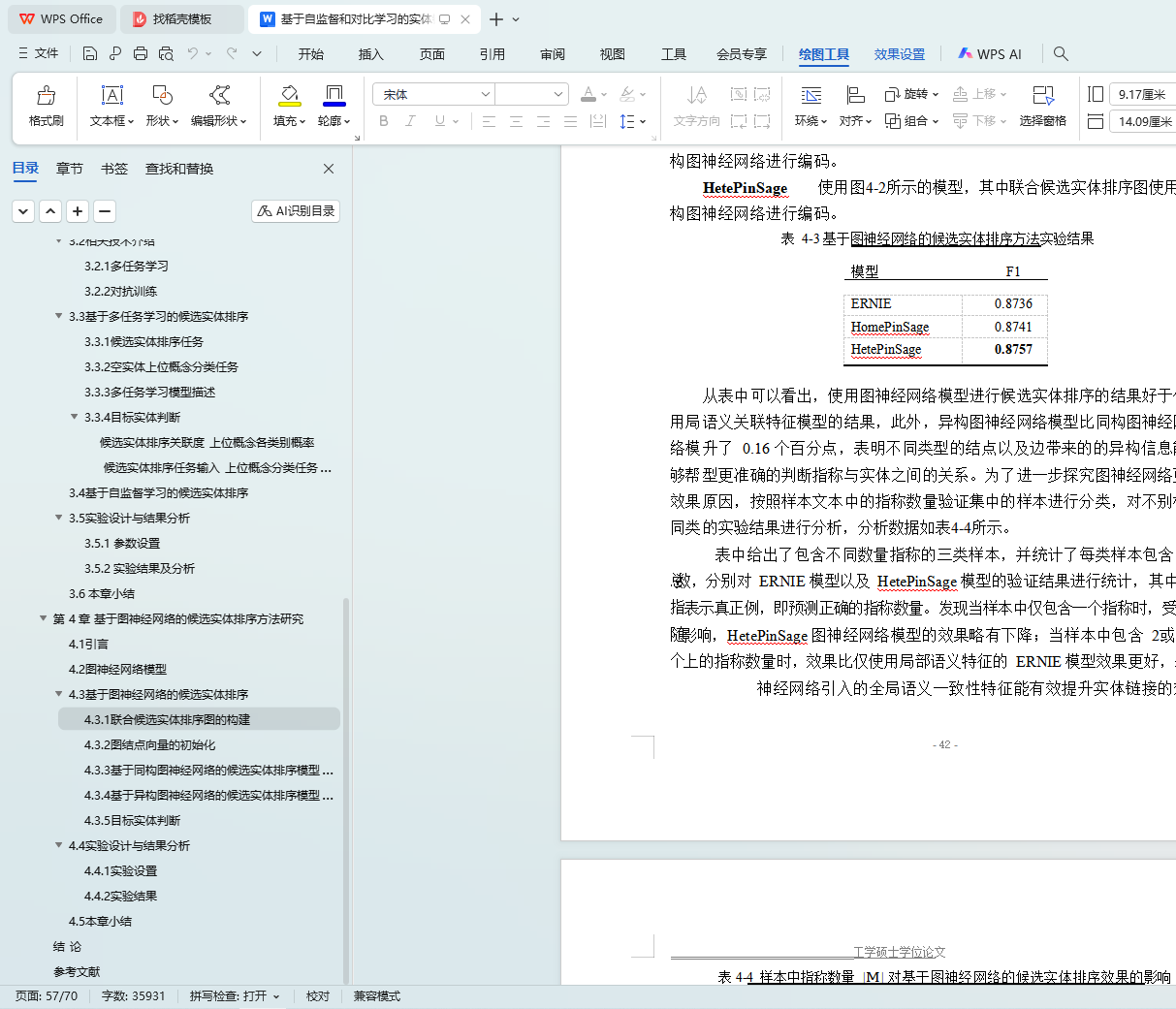
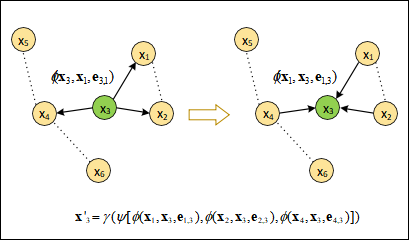
(3) 基于图神经网络的候选实体排序方法研究。当一个文档中存在多个指称时,候选实体排序阶段难以准确建模文档中的所有文本、指称以及候选实体之间的关系,针对这一问题,提出使用实体链接有监督和自监督任务学习图结点的初始化表示,并利用异构图神经网络模型对结点关系进行编码的方法。实
验表明,该方法相较于仅使用局部上下文语义特征或同构图神经网络等方法能取得更好的效果。
关键词:实体链接;语义向量召回;自监督学习;异构图神经网络
Abstract
Knowledge graph is a technique for storing knowledge as structured data, which is widely used in many fields such as natural language processing, recommendation systems, and information retrieval. In this paper, we research on entity linking, the task goal of which is to find semantically consistent mappings between identified mentions in text and entities in the target knowledge graph, so as to eliminate the diversity and ambiguity of natural language. Entity linking is a key technique in the process of knowledge graph construction and application. Entity linking is usually divided into two stages: candidate generation and candidate ranking. The commonly used methods for candidate generation rely on entity alias lists, which are labor-intensive and time-consuming to construct and optimize, and difficult to migrate between different domains. And for candidate ranking, the existing methods have the following problems: 1). candidate ranking methods based on pre-training models cannot accurately learn the association between denotational features and entity features because of the differences between pre-training tasks and entity linking tasks; 2). Those methods based on graph representations fail to accurately model the relations of text, mentions, and relationships among candidate entities in a document. In this paper, the following research is conducted to address these problems and challenges:
(1) Research on candidate generation methods. For the diversity of candidate entity
names, the string-based matching method and the semantic vector retrieval-based method are researched respectively. Some names of candidate entities usually have the same prefix or suffix, based on this feature, this paper proposes the method of using a trie tree to build an entity alias index for prefix and suffix matching to achieve a higher recall rate with less extra computational cost. In this paper, we propose a method to semantically encode entities based on a pre-trained language model, and then complete the candidate generation by semantic vector approximate nearest neighbor(ANN) search. Experiments show that using semantic vector ANN search when entities lack alias lists can improve the effectiveness of candidate generation.
(2) Research on candidate ranking methods based on self-supervised learning. For the candidate ranking stage, existing methods use pre-training models to learn semantic associations between denotational contexts and candidate entity features, and the objective
function and data features used in the pre-training task are significantly different from the entity linking task, and in order to eliminate the effect of such differences, this paper proposes a candidate ranking method based on self-supervised learning, using existing large-scale knowledge graphs to construct a discriminative self-supervised learning task related to entity lingking. In addition, adversarial training and multi-task learning are used to further improve the generalization of the model. Experiments show that the accuracy of entity linking can be effectively improved based on the self-supervised task.
(3) Research on candidate ranking methods based on graph neural networks. To address the difficulty of accurately modeling relationships among all the text, mentions and candidate entities in a document in the candidate ranking stage, a heterogeneous graph neural network model is adapted, and the initialized representation of graph nodes is learned with supervised and self-supervised tasks. Experiments show that this method works better compared to methods such as using only local contextual semantic features or homogeneous graph neural networks.
Keywords: Entity Linking, Semantic Vector Search, Self-supervised Learning, Hetero- geneous Graph Neural Network
摘 要 I
Abstract III
第 1 章 绪论 1
1.1 课题背景及研究意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 2
1.2.1 预训练语言模型 2
1.2.2 候选实体召回 5
1.2.3 候选实体排序 6
1.3 任务定义及数据集 8
1.3.1 任务定义 8
1.3.2 实体链接数据集介绍 9
1.3.3 评价指标 9
1.4 本文主要研究内容 10
1.5 本文结构安排 11
第 2 章 候选实体召回方法研究 13
2.1 引言 13
2.2 基于字符串匹配的候选实体召回 13
2.2.1 实体别名倒排索引表的构建 13
2.2.2 基于字符串模糊匹配的候选实体召回 14
2.3 基于语义向量检索的候选实体召回 16
2.3.1 近似最近邻向量检索算法 16
2.3.2 指称及实体名称语义编码 17
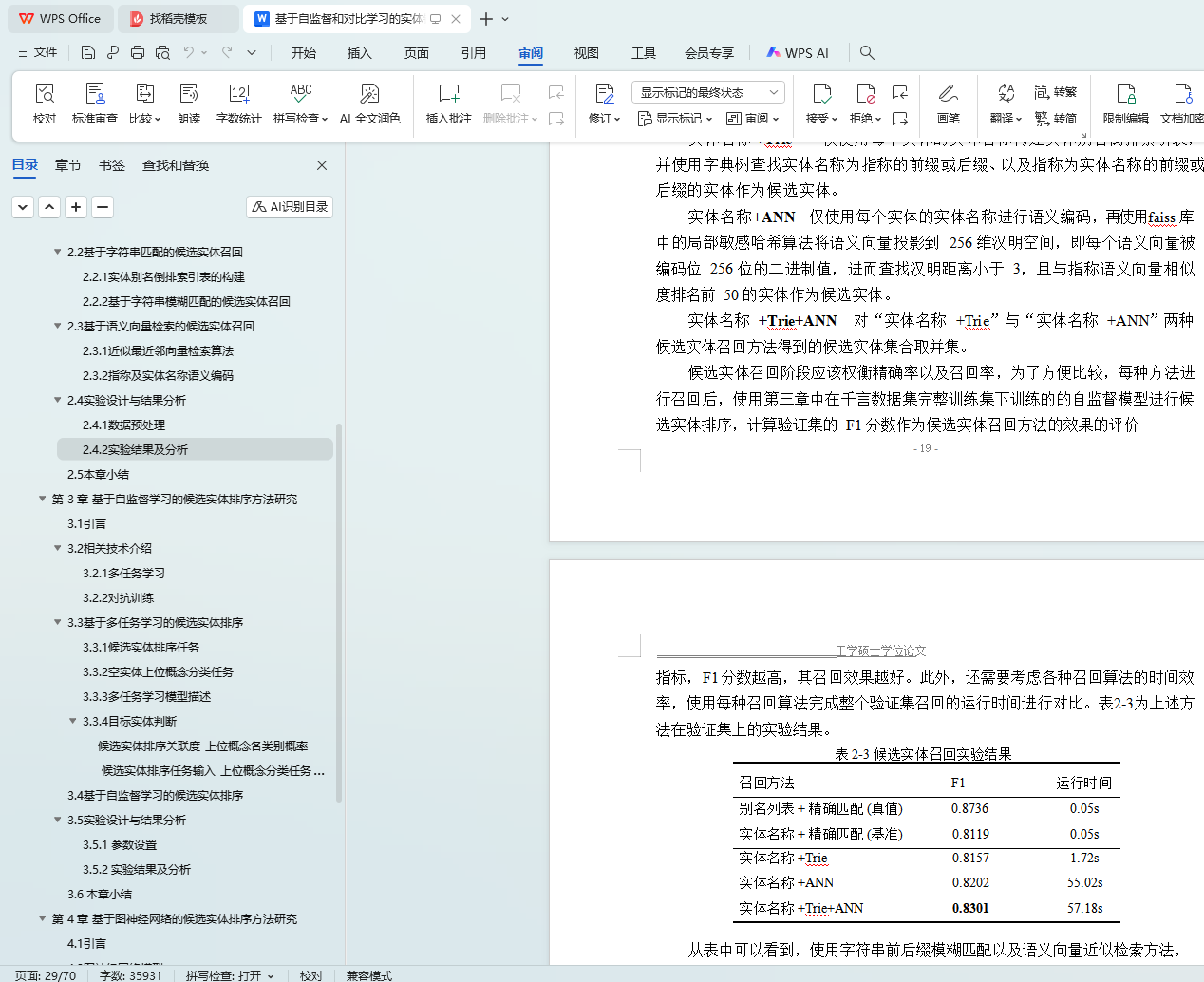
2.4 实验设计与结果分析 19
2.4.1 数据预处理 19
2.4.2 实验结果及分析 19
2.5 本章小结 20
第 3 章 基于自监督学习的候选实体排序方法研究 21
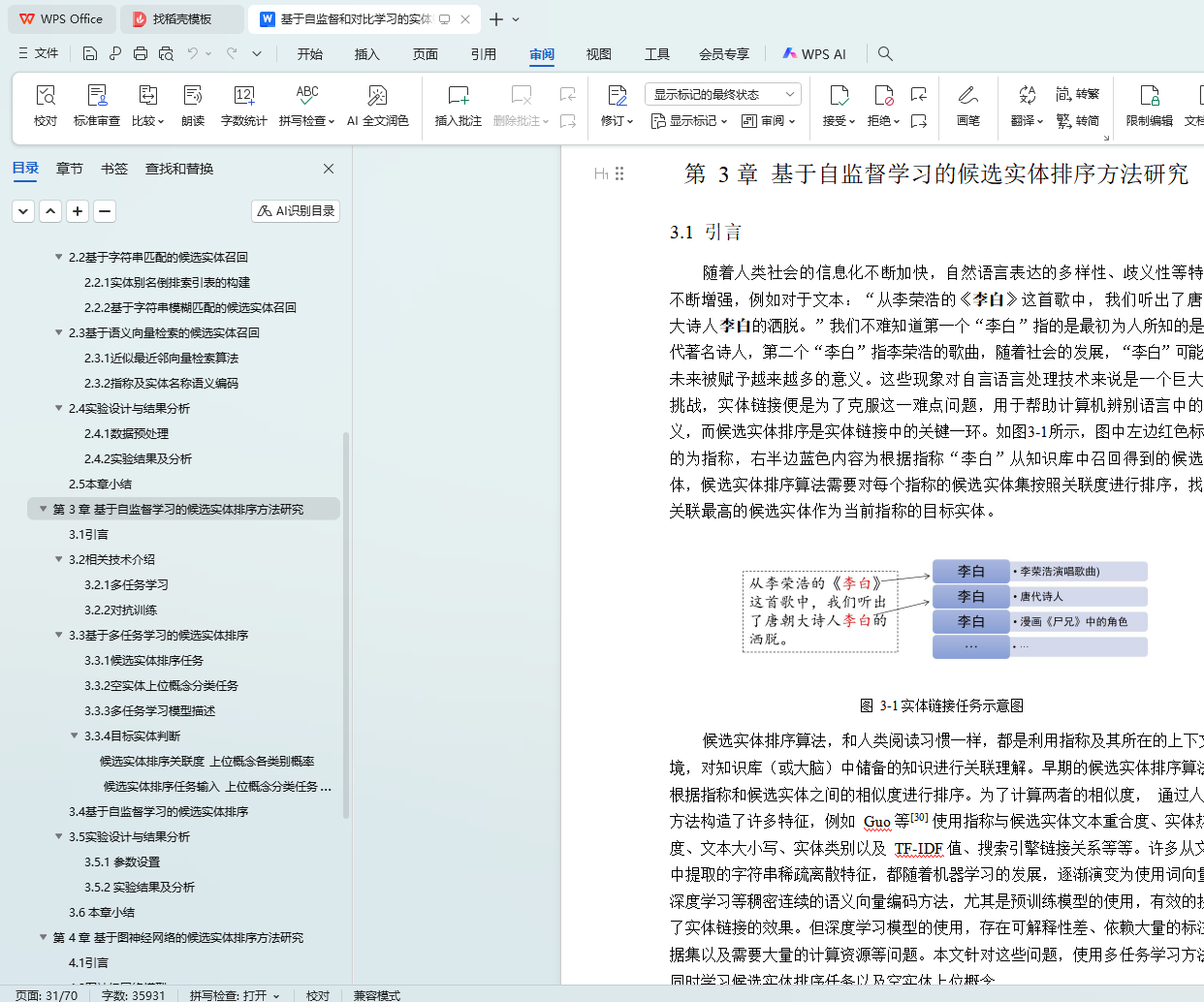
3.1 引言 21
3.2 相关技术介绍 22
3.2.1 多任务学习 22
3.2.2 对抗训练 23
3.3 基于多任务学习的候选实体排序 24
3.3.1 候选实体排序任务 24
3.3.2 空实体上位概念分类任务 26
3.3.3 多任务学习模型描述 27
3.3.4 目标实体判断 27
3.4 基于自监督学习的候选实体排序 29
3.5 实验设计与结果分析 30
3.5.1 参数设置 30
3.5.2 实验结果及分析 31
3.6 本章小结 33
第 4 章 基于图神经网络的候选实体排序方法研究 34
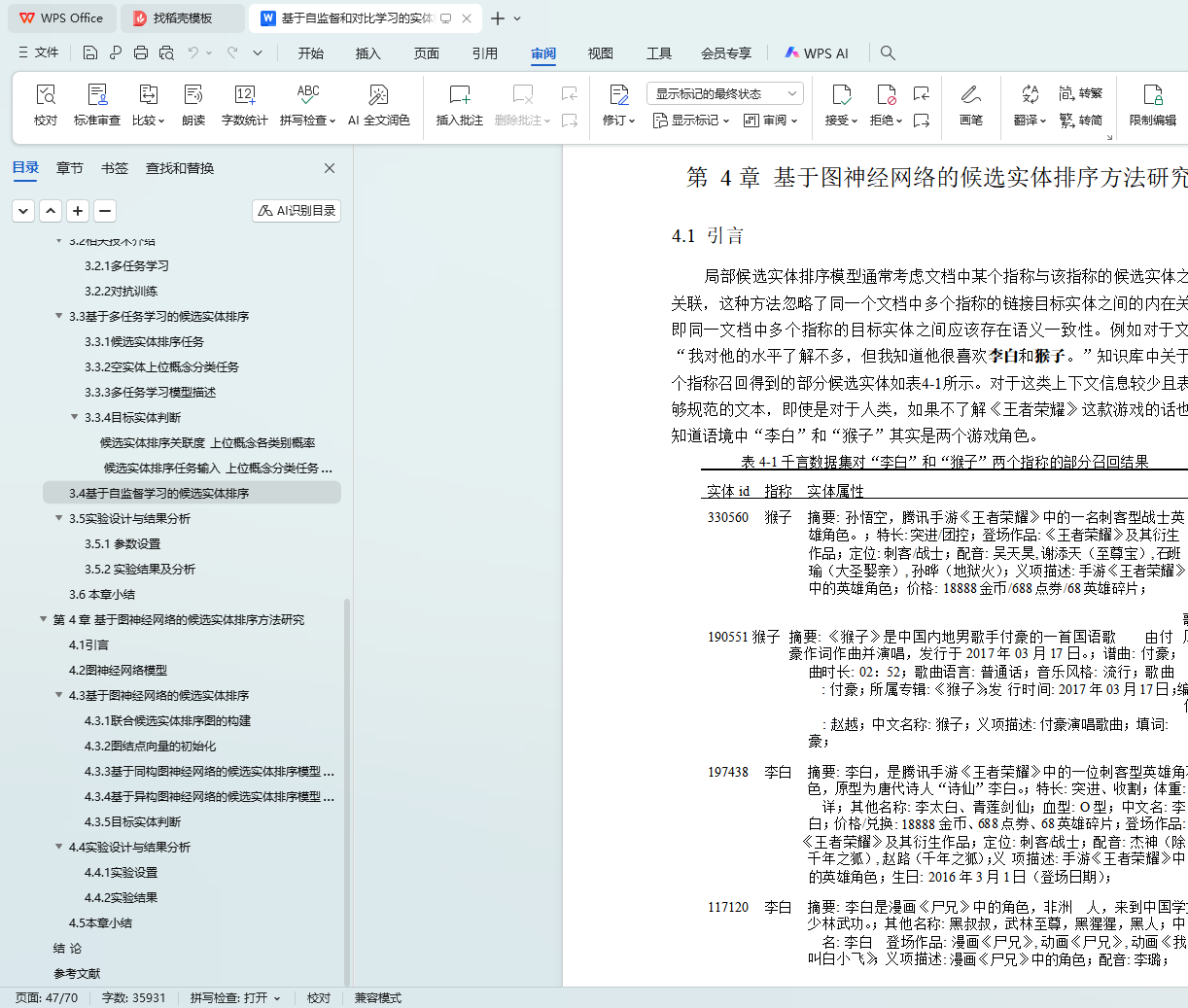
4.1 引言 34
4.2 图神经网络模型 36
4.3 基于图神经网络的候选实体排序 37
4.3.1 联合候选实体排序图的构建 37
4.3.2 图结点向量的初始化 38
4.3.3 基于同构图神经网络的候选实体排序模型描述 39
4.3.4 基于异构图神经网络的候选实体排序模型描述 40
4.3.5 目标实体判断 41
4.4 实验设计与结果分析 41
4.4.1 实验设置 41
4.4.2 实验结果 42
4.5 本章小结 43
结 论 44
参考文献 45
致 谢 54